Do you know the difference between a cap screw and a machine bolt? You’re in the right place if you love DIY projects or are simply curious about hardware items. Both cap screws and machine bolts are widely used in various construction projects, and the terms are often used interchangeably. However, they are different in various ways and serve different purposes. In this blog post, we’ll be examining the differences between these two hardware tools.
What is Cap Screw?
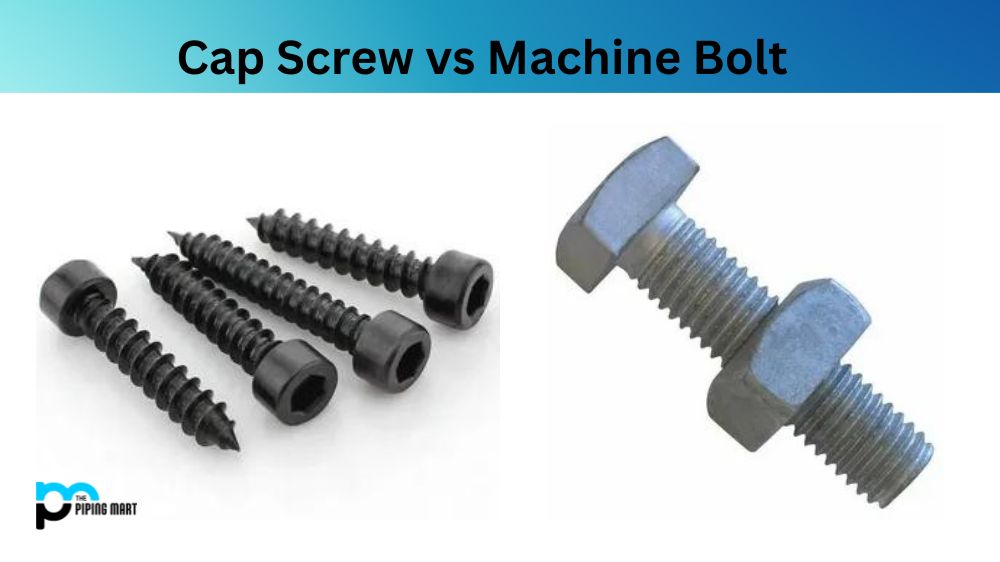
A cap screw is a fastener consisting of a threaded bar or rod with either an internal or external head. Internal heads are typically hexagonal or square in shape, while external heads can be round, hexagonal, slotted, cheesehead and countersunk. They commonly attach machine parts, providing strength and better alignment than normal screws with tapped threads. Cap screws differ from regular screws in that they are usually more precise due to their accurate thread diameter and length and stronger because they’re made from higher-grade metals such as alloy steel or stainless steel.
What is Machine Bolt?
A machine bolt is an externally threaded fastener designed with a nut to assemble two or more components. They are made from various materials, including steel, aluminium and stainless steel. Machine bolts typically include hex heads and full threads, which allows them to create strong and durable joints between components. Their versatility makes them one of the most commonly used fasteners in industrial applications.
Difference Between Cap Screw vs Machine Bolt
Thread Type
A significant difference between cap screws and machine bolts is their thread type. Cap screws are generally made with a coarse thread, while machine bolts have a fine thread. The difference in thread types is mainly due to their purpose. Cap screws are designed to be used as a bolt, while machine bolts are created for threading into internal threads, such as a tapped hole.
Head Shape
Another difference between cap screws and machine bolts is the shape of their heads. Cap screws have a rounded head with a flat or smooth top, while machine bolts have a hexagonal head that requires a wrench. The rounded head of a cap screw makes it sit flush against the surface it is attached to, while the hexagonal head of a machine bolt makes it easy to tighten and remove.
Length and Size
The length and size of the cap screw and machine bolt also differ. Cap screws are typically shorter and thicker screws, while machine bolts are longer and thinner than their counterparts. Cap screws are generally used when a fastener needs to be shorter and stronger, while machine bolts are necessary when you need a longer and thinner screw.
Material
Lastly, there is the question of material. Both cap screws and machine bolts can be made from various materials, such as stainless steel, brass, or aluminium. However, cap screws are typically made from stronger materials since they are often used in high-stress situations. Meanwhile, machine bolts are often made from materials that are easier to cut and thread.
Application
The above mentioned differences show that cap screws and machine bolts are designed for different purposes. Cap screws are often used in high-stress and load-bearing applications, while machine bolts are perfect for applications requiring a flush or countersunk finish. Knowing these differences can help you pick the right tool for your project.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the difference between cap screws and machine bolts may not be apparent to everyone, but they are an essential distinction for those in the hardware and construction business. Each screw has a specific purpose, and using the right tool for the job is essential. This blog post has been informative and enlightening for those new to the hardware and DIY world. Remember, it’s always best to consult with a professional if you are unsure which screw to use for your project.
Rachana is a dedicated and ambitious young woman who has made a name for herself in the metal industry. From her earliest days in the industry, Rachana showed a natural talent for problem-solving and a keen eye for detail. In her free time, She enjoys reading up on the latest advancements in the industry, as well as exploring new ways to innovate and improve upon existing processes.