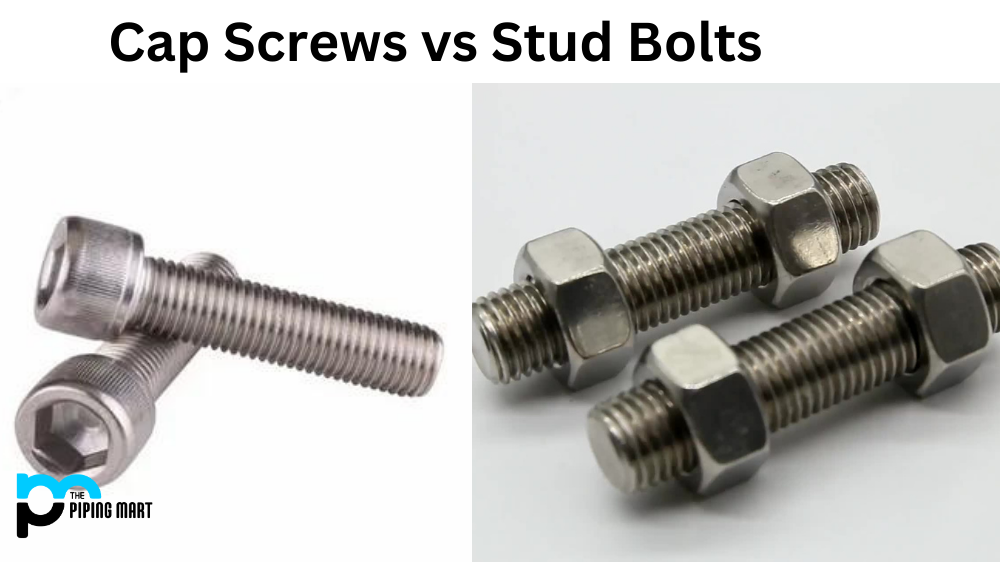
Cap screws and stud bolts are fasteners frequently used in mechanical and structural applications. They both serve the same purpose: securing objects, but they differ in design and application. This blog post will explore the differences between cap screws and stud bolts, including their functions, features, and advantages.
What is Cap Screw?
A cap screw, also known as a socket head cap screw, is a threaded fastener with a cylindrical head and a hexagonal socket. It is designed to be tightened or loosened using an Allen wrench or a hex key. Cap screws are typically used in applications where a robust and precise holding force is needed and access is restricted, such as in machinery, equipment, and electronics. Depending on the requirements, they come in various sizes, materials, and finishes and can be fully or partially threaded.
What is Stud Bolt?
A stud bolt, also known as a threaded rod, is a type of fastener that consists of a long, threaded rod with threads on both ends and two hexagonal nuts. It is used for applications that require a robust and permanent connection, such as in piping, construction, and automotive industries. Stud bolts are inserted into pre-drilled holes, secured with nuts on both ends and may be coated with a layer of zinc or other material to prevent corrosion.
Difference Between Cap Screws and Stud Bolts
Functionality
Both cap screws and stud bolts serve the same purpose: to secure objects in place with a solid and lasting bond. However, they differ in functionality. Cap screws primarily attach one thing to another, while stud bolts connect two objects. For example, a cap screw secures a machine part onto a surface, while a stud bolt connects two flanges in a pipeline.
Advantages
The advantages of using cap screws are that they provide a high clamping force, are easy to install, and have a low-profile head that can fit into tight spaces. Additionally, cap screws are ideal for frequent disassembly applications, as they can be easily removed and reinstalled. On the other hand, the advantages of using stud bolts are that they provide a permanent and stable connection, even under high-stress loads. Furthermore, stud bolts offer more flexibility in length, as they can be cut to size and used in any application.
Conclusion
Cap screws and stud bolts are two fasteners essential in mechanical and structural applications. While they serve the same general purpose, their design and application differ. Cap screws are designed for robust and precise holding force and are ideal for tight access areas, while stud bolts are suitable for permanent, high-stress connections. Ultimately, the choice between cap screws and stud bolts depends on the application’s requirements, including the load capacity, access, and connection longevity. Knowing the differences between these fasteners can help you make an informed decision and ensure a successful outcome for your project.

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.