Nuts are an essential part of any fastening system. They secure bolts and ensure the joint is not loosened or detached. While there are plenty of options available, castle nuts and nylock nuts are two popular types of nuts used for fastening. Although both serve the same purpose, their differences affect their functionality in various situations. This blog post will discuss the differences between castle nuts and nylock nuts, highlighting their unique features and best use cases.
What is Castle Nut?
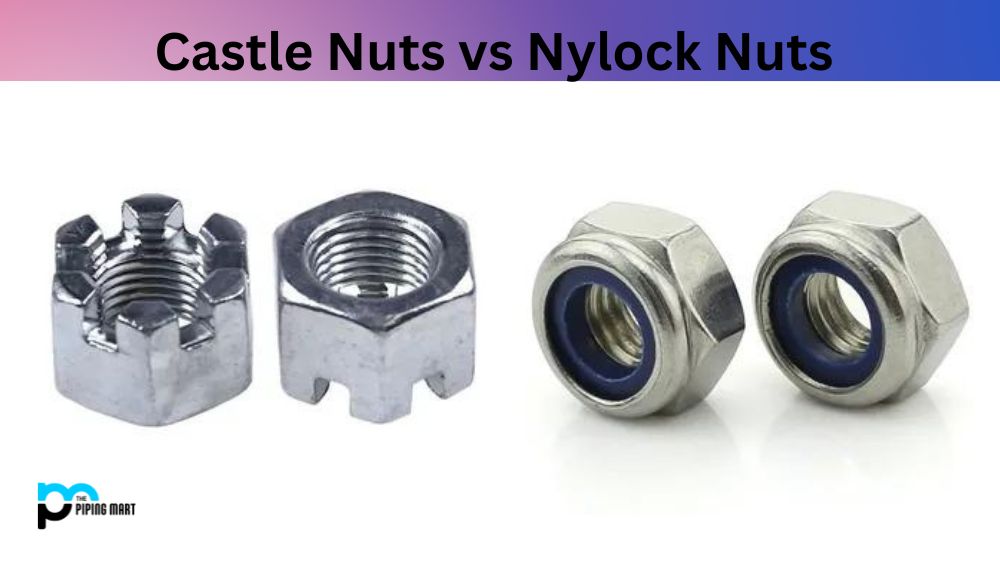
A Castle Nut, a slotted or castle wheel nut, is a fastener used to secure components and assemblies. It has two notches cut into its sides so that the component it secures cannot be loosened when it is tightened with a cotter pin or wire. They are commonly used in automotive applications, machinery construction and bicycle frames. The name is derived from its shape, which resembles an ancient fortification tower (“castle”).
What is Nylock Nuts?
Nylock nuts are used in fastening applications with nylon-insert locking technology to reduce the risk of loosening due to vibration. They consist of an outer hexagonal metal shell and an inner nylon insert, which creates friction between threads and prevents them from unscrewing. Nylock nuts come in various sizes and materials, ranging from steel and stainless steel to brass and aluminium, making them suitable for almost any application.
Difference Between Castle Nut and Nylock Nuts
Structure
Castle nuts are hexagonal and have slots at the top, which are used to secure a cotter pin to keep the nut from backing off. On the other hand, nylock nuts are hexagonal, with a nylon insert located at the top of the nut. The nylon insert provides a locking mechanism that prevents the nut from backing out or coming loose due to vibration.
Functionality
Castle nuts are commonly used when it’s essential to secure a bolt that’s regularly adjusted or removed, such as in the case of wheels, steering parts, and suspension parts. The cotter pins can easily be removed and replaced, allowing access to the nut. Nylock nuts, on the other hand, are used when the joint is likely to experience many vibration forces, thus increasing the chance of the nut coming loose. They are ideal for applications where loosening is a safety concern.
Tightening Method
Castle nuts are tightened with a socket wrench and then secured with a cotter pin inserted through the slots mentioned earlier. Nylock nuts, on the other hand, can be hand-tightened thanks to the nylon insert locking mechanism. This feature makes them ideal for situations where accessing and turning the bolt’s nut is difficult.
Material
Castle nuts are typically made of steel or iron, while the nylon insert in nylock nuts is made of nylon. This feature makes nylock nuts more expensive than castle nuts. Nuts of steel or iron have high tensile strength, making them ideal for heavy machinery and applications requiring significant force to hold the joint in place.
Reliability
Regarding reliability, both castle nuts and nylock nuts are dependable fastening solutions. The cotter pin used in the castle nut system is an extra layer of security against the nut coming loose. Similarly, the nylon insert in nylock nuts holds them tightly in place, reducing the risk of loosening and detachment.
Conclusion:
In summary, castle nuts and nylock nuts differ in their structure, functionality, tightening methods, material, and reliability. Castle nuts are ideal for regular adjustments, while nylock nuts are suitable for joints prone to vibration or loosening. Castle nuts are more suitable for applications that require significant force to hold the joint in place due to their structural makeup. Nylock nuts are more expensive but offer a more secure mechanism for locking fasteners in place. Ultimately, the decision on which type of nut to use depends on the specific application and the level of security required.