For any Flange or any product to perform properly it is fundamental to choose the right flanges for the job. The flange should fit in perfectly into the pipe joints in order to conduct its functions correctly. A minor mistake in selecting a flange may have an effect on an application resulting in an expensive mistake. Let us discuss the factors that are all associated in selecting the right flange for the correct application to ensure maximum usability.
Types
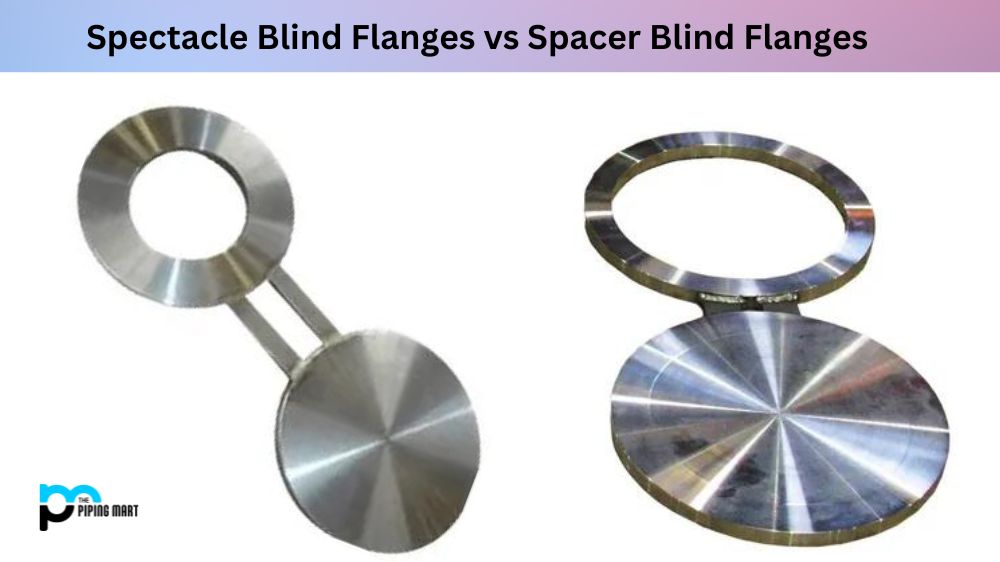
It’s fairly easy to spot the type of flanges by the way it looks. First classify the top of the flange by deciding whether the flange has a welded neck, threaded bore, lap joint, flat face, socket weld, or tongue and groove. Next, the bottoms are identified by evaluating whether they have a flat face, which is completely flat, or a raised face, which is a slightly raised section on the face of the flange.
Types of Flanges
Size
The size of the flange consists of factors that include the standard used (: DIN – Deutsches Institut für Normung / European, ANSI – American National Standards Institute, and JIS – Japanese International Standard), the pressure level needed, and the actual size of the flange. Factors include the inner diameter, the outer diameter, the number of bolt holes, the diameter of the bolt hole and the bolt circle.
Thickness
Rely on the thickness of the flanges, it can be determined how high a pressure it can handle, in any applications thicker flanges can resist higher pressures.
Bolt Holes
Bolt Holes enables to measure the size of the flange and the pressure class. The number of bolt holes, the pitch circle diameter, and the actual size of the bolt holes on the flange are 3 factors that need to be addressed. If the bolt is thicker and stronger it can more pressure.
Standards
There are a various standards from which you can choose these flanges. The flanges will be choosed based upon the application and the standard of the product it will be connected to (i.e. valves) 3 main standards used are: DIN – Deutsches Institut für Normung / European, ANSI – American National Standards Institute, and JIS – Japanese International Standard.
Pressure Class
The pressure class is a critical indicator of the maximum pressure a flange can endure and operate safely. Various standards offer multiple pressure levels, ranging from low to high tolerance. It’s crucial to match the pressure rating of the flange with that of the pipes and valves in the system it connects to. Aligning these pressure specifications ensures the seamless integration of flanges, maintaining safety and optimal functionality within the overall piping process.
Materials
It is the most important to choose the right material for a flange depending upon the application and understanding the elements it will encounter in an application that the piping system is being used. (Pressure, moisture, corrosion, temperature) Common materials include stainless steel, duplex steel, carbon steel, and copper nickel, etc.
Conclusion:
When selecting flanges, prioritize factors like material compatibility, pressure and temperature requirements, facing type, size, and standards compliance. Consider the application’s corrosion resistance needs and the fluid type. By attentively weighing these aspects, you ensure the chosen flanges align with the specific demands of your piping system. This meticulous consideration guarantees longevity, efficiency, and safety in your industrial operations, offering a reliable and well-matched solution for your unique requirements.

Pipingmart is B2B portal specializes in industrial, metal and piping products. Also, share latest information and news related to products, materials and different types grades to help business dealing in this industry.