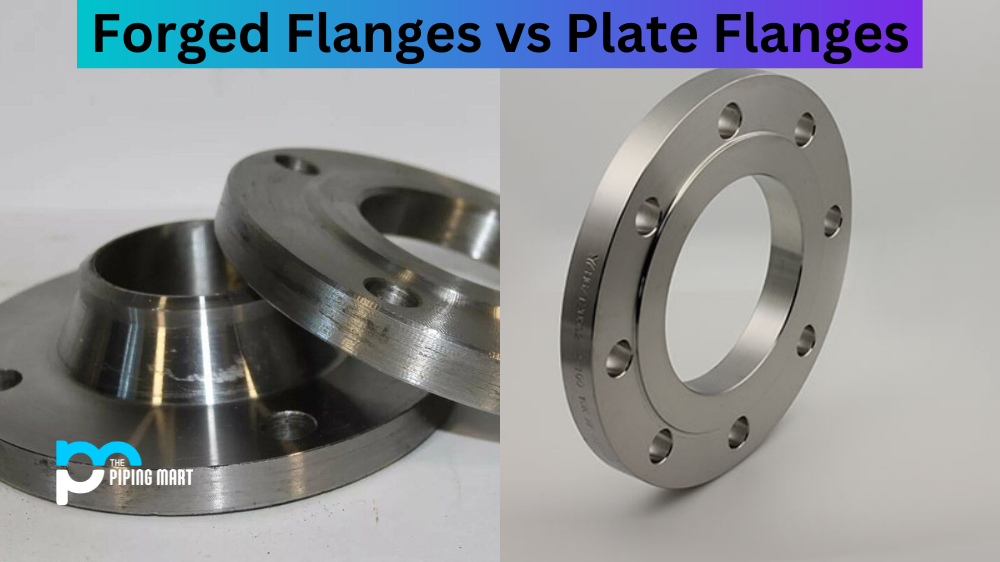
Flanges are essential components in piping systems. That connect Pipes, Valves, and Equipment. They provide a secure and leak-free connection and allow easy access for maintenance and repair. Flanges come in different types, materials, and manufacturing methods. Each with unique features and advantages. In this blog post, we’ll compare two popular flanges: forged and plate flanges. We’ll discuss their differences, benefits, and applications to help you choose the type for your piping system.
Forged Flanges
Forged flanges encompass diverse types like Weld neck, Slip-on, Blind, Socket weld, Threaded, and Lap joint. Each offering distinct advantages ranging from high-pressure capabilities to exceptional corrosion resistance. Tailoring to specific application needs. Forged flanges are available in various materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, and nickel alloys. This variety ensures compatibility with various industrial requirements, emphasizing their versatility and suitability across different sectors.
Plate Flanges
Plate flanges, often called flat flanges, are crafted from flat plates. Meticulously cut and drilled to align with specific flange dimensions and bolt holes. Typically, lighter and thinner than their forged counterparts. Plate flanges are widely employed in low-pressure and non-critical applications like water supply, irrigation, and HVAC systems. Renowned for cost-effectiveness, plate flanges offer an economical alternative for budget-conscious projects. Varieties such as Slip-on, Lap joint, Blind, and Threaded flanges cater to diverse needs, with material options including carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, depending on specific application requirements.
Plate Flange Standard
Plate flanges adhere to recognized standards like ASME B16.5 or EN 1092-1, ensuring uniformity in dimensions and specifications. These standards establish criteria for the size, pressure ratings, and materials used in plate flange manufacturing. Adhering to a standardized framework facilitates seamless integration into diverse piping systems, enhancing compatibility and reliability in industrial applications.
Difference Between Forged Flanges and Plate Flanges
The main differences between forged flanges and plate flanges include the following:
Manufacturing method
Forged flanges are made from raw materials using a forging machine, while plate flanges are cut and drilled from a flat plate.
Strength and durability
Forged flanges are stronger and more durable than plate flanges. Making them suitable for high-pressure and critical applications.
Corrosion resistance
Forged flanges are more resistant to corrosion and wear than plate flanges. Due to the forging process and material selection.
Cost
Forged flanges are more expensive than plate flanges due to their higher strength, customization, and material selection.
Other Differences
- Forged flanges are made from solid metal, while plate flanges are made from flat pieces.
- Forged flanges are typically stronger than plate flanges.
- Plate flanges are typically less expensive than forged flanges.
- Forged flanges can be made in various shapes, while plate flanges are limited to a few basic shapes.
- Forged flanges can be made from various metals, while plate flanges are typically carbon or stainless steel.
- Forged flanges typically have a smoother finish than plate flanges.
- Plate flanges are easier to install than forged flanges.
- Forged flanges have a longer lifespan than Plate flanges.
Conclusion
Forged and plate flanges exhibit distinct advantages tailored to specific application needs. Forged flanges boast high Strength, Durability, and Corrosion resistance, making them ideal for rigorous conditions like high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Meanwhile, plate flanges offer a cost-effective solution in less demanding scenarios, where strength and durability are secondary considerations. When deciding between the two, weighing factors such as application requirements, budget constraints, and expected lifespan is crucial to establishing a secure, dependable, and efficient piping system.

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.