Electrical wiring is one of the most important components of any building or project. One important factor to consider when wiring your project is the current carrying capacity of copper cables in sq mm. Knowing this information can help you make sure that your wiring project is safe, effective, and up-to-code. Let’s take a look at what current carrying capacity means and how it relates to copper cables.
What is the Current Carrying Capacity?
Current carrying capacity (also known as ampacity) measures the maximum amperage that a cable can handle without suffering damage or overheating. The higher the current carrying capacity, the more power a cable can handle before it needs to be replaced or upgraded. This makes current carrying capacity an essential measurement for any wiring project.
How Does It Relate To Copper Cables?
When deciding on which type of wire to use for a project, many people turn to copper because it is a great conductor of electricity and heat. However, not all copper wires are created equal—each type has its own current carrying capacity rating based on its size/diameter and insulation rating. The most commonly used sizes in sq mm range from 0.5 sq mm to 1000 sq mm, with each size having its own specific ampacity rating depending on the insulation material used (which ranges from PVC or rubber). It’s important to make sure you know what size wire you need for your particular application, so you don’t overload your circuit.
These major determining factors are:
Conductor Size:
The larger the circular mil area, the greater the current capacity.
The amount of heat generated should never exceed the maximum temperature rating of the insulation.
Ambient Temperature:
The higher the ambient temperature, the less heat required to reach the maximum temperature rating of the insulation.
Conductor Number:
Heat dissipation is lessened as the number of individually insulated conductors, bundled together, is increased.
Installation Conditions:
Restricting the heat dissipation by installing the conductors in conduit, duct, trays or raceways lessens the current carrying capacity. This restriction can also be alleviated somewhat by using proper ventilation methods, forced air cooling, etc.
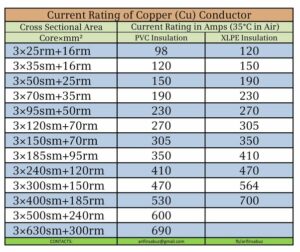
The table below shows some common copper cable sizes and their respective ampacity ratings:
Conclusion
When working on any electrical wiring project, understanding the current carrying capacity of different types of copper cables is essential for safety and efficiency purposes. As we have seen above, different sizes of copper cables have different ampacity ratings depending on the insulation material used with them—it’s important to make sure that you select the right size wire for your application so that you don’t overload your circuit! With this information in mind, you can ensure all your electrical wiring projects are done correctly and safely!

A passionate metal industry expert and blogger. With over 5 years of experience in the field, Palak brings a wealth of knowledge and insight to her writing. Whether discussing the latest trends in the metal industry or sharing tips, she is dedicated to helping others succeed in the metal industry.