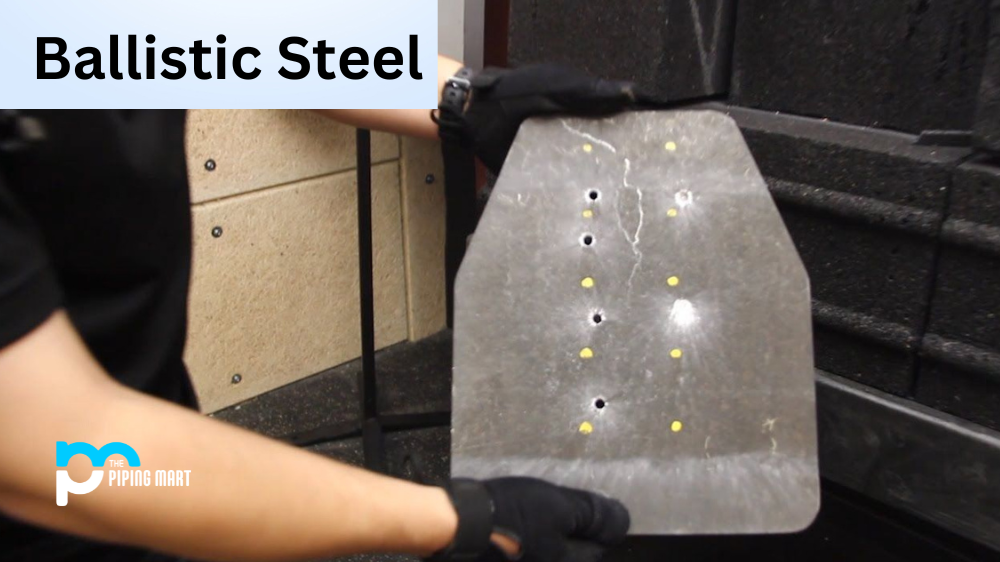
Ballistic steel is used for manufacturing protective armor, such as bulletproof vests and helmets. This kind of steel has a high degree of hardness that helps it absorb the impact of projectiles and other objects. Read on to find out how ballistic steel is made and why it’s so effective in protecting people from harm.
How is ballistic steel made?
Manufacturing Process
The process begins with selecting raw materials, typically a combination of iron ore, carbon, and chromium. The iron ore is melted in an electric arc furnace at temperatures exceeding 2,400°F (1300°C). This molten material is then poured into molds, where it cools and solidifies into ingots. These nuggets are then rolled into thin sheets that can be further processed into plates or bars.
The next step involves the heat treatment process. This involves heating the steel to around 1,700°F (925°C) before quenching it in water or oil. The rapid cooling causes the metal to become incredibly hard and resilient—an essential trait for ballistic steel. After this, the steel is tempered to reduce its brittleness before being cut into shapes suitable for body armor applications.
Mining
The first step in the manufacturing process is mining the iron ore. The iron ore is then smelted in furnaces where the impurities are removed, and carbon is added.
Refining
The next step is refining the iron in a furnace to remove impurities and increase the carbon content. The iron is then cast into ingots or billets.
Rolling and Forging
The ingots or billets are then rolled into thin sheets or plates. The plates are then forged into the desired shape, such as a bulletproof vest panel.
Heat Treatment
The final step in the manufacturing process is heat treatment, which helps improve the steel’s ballistic properties.
Why It Works
Ballistic steel works because of its incredible strength and resilience when struck by an object traveling at high velocities. The metal absorbs the impact energy from these objects instead of being transferred to whatever lies beneath it—in this case, a person’s body wearing armor made with ballistic steel plates or bars. This absorption helps prevent injuries like broken bones or organ damage that would otherwise occur if a person wore inadequate protection, such as Kevlar alone.
Conclusion:
Ballistic steel has been used for decades in the production of body armor due to its superior strength and ability to absorb impacts from projectiles traveling at high velocities without transferring the energy to whatever lies beneath it—in this case, a person’s body wearing armor made with ballistic steel plates or bars. This makes ballistic steel an ideal choice for anyone looking for reliable protection against potential threats in their line of work or everyday life activities. Understanding how ballistic steel is made can help you decide which type of armor best suits your needs and provide adequate protection from harm when necessary.