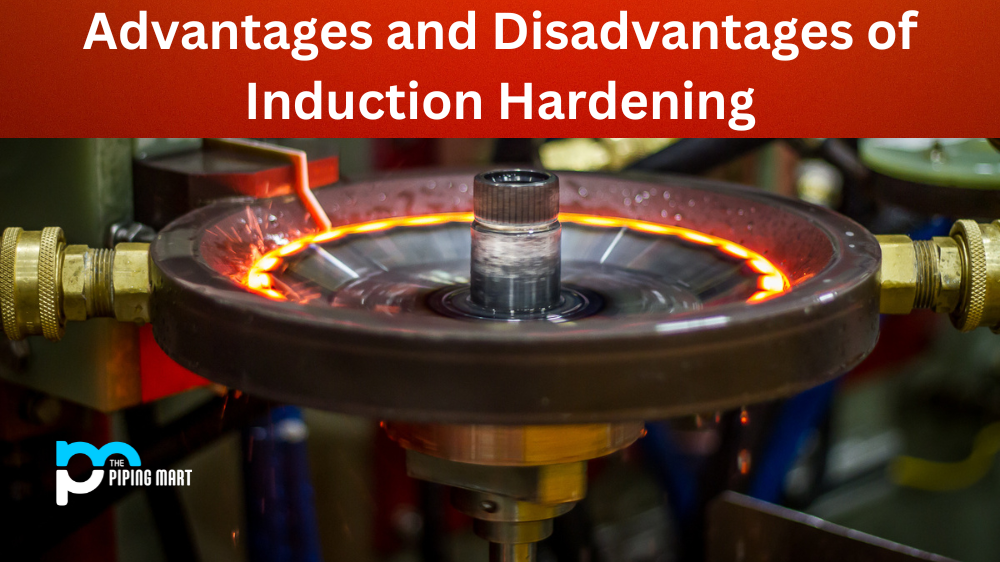
Induction hardening is a process in which an object is heated quickly to a high temperature and then cooled rapidly in order to create hardened surfaces on the object. This process produces extremely strong parts that are resistant to wear and tear. But there are both advantages and disadvantages associated with induction hardening. Let’s take a closer look at them.
Advantages of Induction Hardening
One of the biggest advantages of induction hardening is its speed. This process can be completed much faster than other heat-treating processes, such as case hardening or nitriding, making it ideal for high-volume production runs. Additionally, induction hardening does not require any additional materials such as salt baths or gas tanks, like other heat-treating processes might, thus saving time and money. Furthermore, induction hardening produces a uniform finish across the entire part, so you don’t have to worry about inconsistencies in your parts’ finish.
Increases the hardness of the metal
Induction hardening is a process that increases the hardness of the metal by heating it with an electromagnetic field. This process allows for a more uniform heat treatment, which results in a harder metal.
More durable
The increased hardness of the metal makes it more durable and resistant to wear and tear. This makes induction hardening ideal for components that are subject to high levels of stress or friction.
Improves fatigue resistance
Induction hardening also improves the fatigue resistance of the metal, making it less likely to fail under repeated loads. This is due to the fact that the process creates a more homogeneous microstructure, which is less susceptible to failure.
Reduces distortion
Another benefit of induction hardening is that it reduces distortion. This is because the process can be controlled more precisely, resulting in less heat being applied to the metal. As a result, there is less chance for the metal to warp or deform during the cooling process.
Cost-effective
Induction hardening is also cost-effective, as it is a relatively quick and simple process. Additionally, there is no need for expensive equipment or specialized skills, making it an accessible option for many businesses.
Another advantage of induction hardening is its accuracy. Unlike other heat-treating processes, this method does not require any manual intervention from operators; instead, it uses computer controls to precisely control the temperature and duration of the process. This ensures that each part receives exactly the same amount of heat treatment every time it is produced.
Disadvantages of Induction Hardening
The main disadvantage of induction hardening is its cost. While this method is cheaper than some other heat treating methods in terms of raw materials used and labour required, it still requires expensive equipment such as specialized furnaces and generators in order to perform properly. Additionally, because this process requires electricity rather than fuel sources like gas or oil, running costs can be quite high over time due to energy consumption expenses.
Higher Cost
One of the primary disadvantages of induction hardening is that it is generally more expensive than other heat treatment processes. This is due to the fact that induction hardening equipment is typically more expensive than other types of heat treatment equipment. Additionally, induction hardening generally requires more time and labour than other heat treatment processes.
Limited Thickness
Induction hardening is also generally limited to thinner materials than other heat treatment processes. This is due to the fact that induction hardening works by heating the surface of a material rather than the entire material. As a result, thicker materials are more difficult to heat evenly, which can lead to uneven hardness or even cracks.
Limited to Ferrous Metals
Induction hardening is also generally limited to ferrous metals, such as iron and steel. This is due to the fact that induction hardening relies on magnetic fields to generate heat, and ferrous metals are the only materials that are affected by magnetic fields. Non-ferrous metals, such as aluminium or copper, cannot be induction hardened.
Requires Specialized Equipment
Another disadvantage of induction hardening is that it requires specialized equipment that is not always readily available. Induction hardening equipment can be expensive and may not be available from all heat treatment providers. Additionally, some types of induction hardening equipment may require special training or certification to operate correctly.
Conclusion:
Induction hardening has both advantages and disadvantages when compared to traditional heat-treating methods; however, overall, it remains an effective way to produce hardened surfaces on objects quickly and accurately with minimal manual intervention required from operators during the process itself. With proper maintenance and care for the specialized equipment involved with induction hardening, businesses can save time and money while producing quality parts for their customers without sacrificing precision or consistency in their finished product.

Pipingmart is a B2B portal that specializes in metal, industrial and piping items. Additionally, we share the latest information and information about materials, products and various types of grades to assist businesses that are involved in this business.