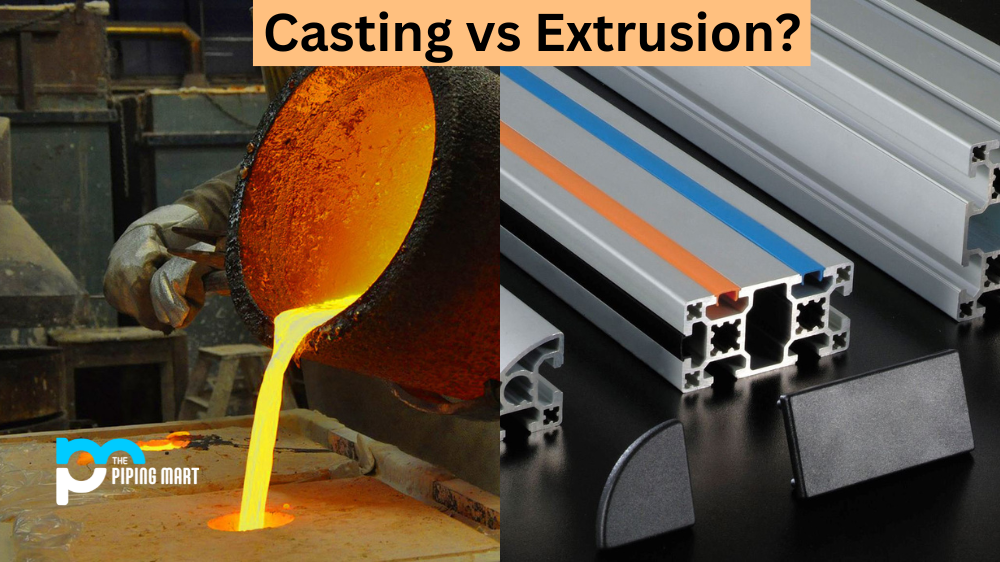
When it comes to manufacturing components or products, there are two main methods of production that you will likely come across—casting and extrusion. Both methods are used in a number of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. But what exactly is the difference between the two? Let’s take a look at how these two processes differ when it comes to producing parts.
Casting
Casting is a process where molten metal or plastic is poured into a custom-made mould that has been designed to create the desired shape. The metal or plastic cools and solidifies in the mould before being removed for finishing operations such as machining or polishing. This method of manufacturing components is ideal for producing high-precision parts with complex shapes and intricate details. It is also suitable for creating large, one-off components that require very little post-processing work. Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is poured into a mould and allowed to solidify. The mould is typically made from metal but can also be made from ceramic or plastic. Casting is often used to create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using other manufacturing methods.
Extrusion
Extrusion is a different type of process, where a material such as metal or plastic is forced through an opening in order to form it into a desired shape. The material passes through the opening at high pressure and temperature, which allows it to be moulded into any shape imaginable. This method of production is great for producing long, continuous parts with consistent cross sections such as tubes, rods, bars, and wires. It can also be used to produce small components with simple shapes thanks to its low cost and high-speed capabilities. Extrusion is a manufacturing process in which a material is forced through a die to create a desired shape. Extrusion can be used with both metals and plastics and is often used to create objects with a constant cross-sectional shape, such as pipes or tubing.
Advantages of Casting
One advantage of casting is that it can be used to create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using other manufacturing methods. Additionally, casting can be used with a variety of materials, including metals, ceramics, and plastics.
Advantages of Extrusion
One advantage of extrusion is that it can be used to create objects with a constant cross-sectional shape, such as pipes or tubing. Additionally, extrusion can be used with both metals and plastics.
Disadvantages of Casting
One disadvantage of casting is that it can be an expensive process due to the cost of the mould. Additionally, casting can be time-consuming, as the mould must be created before the casting process can begin.
Disadvantages of Extrusion
One disadvantage of extrusion is that it can only be used to create objects with a constant cross-sectional shape. Additionally, extrusion may not be suitable for some materials that are not able to withstand the high temperatures and pressures involved in the extrusion process.
Conclusion:
When deciding between casting and extrusion for your next project, it’s important to consider both the design requirements as well as production costs associated with each method. If you need complex parts with intricate details or large one-off components, then casting may be your best bet; while if you need long continuous parts with consistent cross sections, then extrusion might be more suitable for your needs. Ultimately though, whichever process you choose will largely depend on your specific requirements and budget constraints – so make sure to do your research before making any decisions!

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.