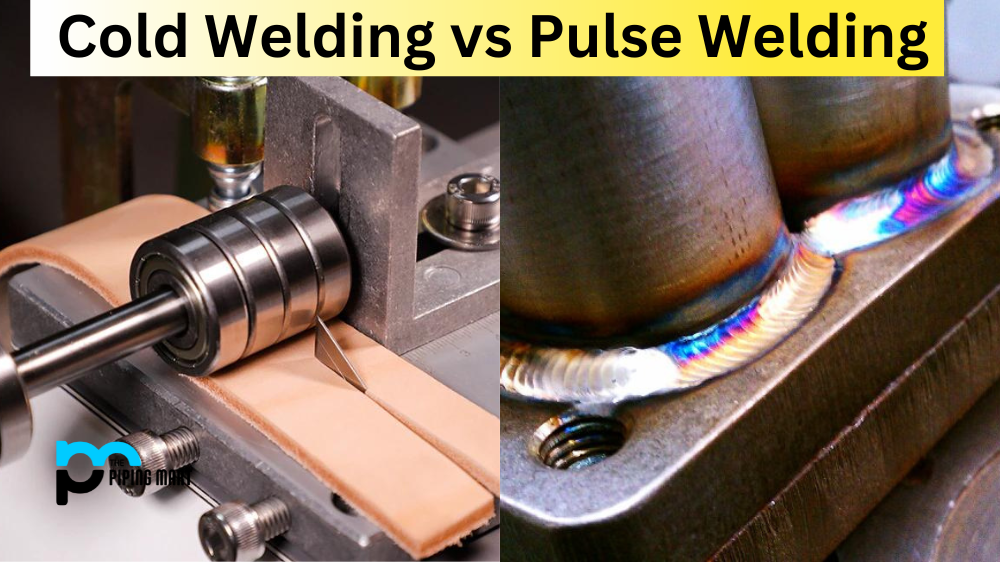
Welding is an essential manufacturing, construction, and daily life process. It is joining two or more pieces of metal through heat and pressure. Two common types of welding used today are cold welding and pulse welding. Although both have similar terms, they differ in terms of processes and applications. This blog will explore the differences between cold and pulse welding, their advantages, and where best to apply them.
What is Cold Welding?
Also known as pressure welding or forge welding, cold welding is a metal-joining process that doesn’t require heat. In cold welding, metals are welded together through pressure alone, causing the atoms to bond at an atomic level. This process is typically used for non-ferrous metals like aluminium, gold, and copper. Cold welding is best for joining metals that can’t be welded with heat or solder and where high conductivity is required.
Advantages
One of the advantages of cold welding is that it doesn’t alter the material’s chemical properties, unlike other welding methods. Another advantage is that it’s cost-effective and environmentally friendly since no heat is required. However, cold welding requires precise cleanliness and surface preparation to adhere to high quality. Also, the pressure needed for the welding must be controlled.
What is Pulse Welding?
Pulse welding is a welding process that uses electricity to join two or more metals. In pulse welding, a series of electrical pulses that generate heat is sent through the metals, enabling them to bond. This process is often used for welding large surface areas. Pulse welding can be used for various ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Advantages
The main advantage of pulse welding is that it produces high-quality welds requiring less energy and time than other methods. Moreover, the process is more consistent and efficient than traditional welding methods since it uses shorter bursts of heat to create the welds. The pulse welding process is also cleaner and leaves less debris, making it an attractive choice for industries conscious of its environmental impact.
Difference Between Cold Welding and Pulse Welding
Applications of Cold Welding and Pulse Welding
The applications of cold welding are best suited for metals that can’t be welded with heat or solder. Cold welding is commonly used in the electrical and electronics industries, particularly for semiconductor manufacturing, bonding electrical leads, and welding cable ends. It is also used in the medical and aerospace industries since it produces high-strength, low-heat welds, making it ideal for precision manufacturing.
Pulse welding, on the other hand, has a broader range of applications in various industries such as automotive, marine, and construction. This process is commonly used for welding stainless steel, aluminium, and copper materials. Additionally, pulse welding is ideal for welding large surface areas such as tanks, heavy machinery, and other equipment.
Other Differences
- Cold welding is a solid-state welding process in which two clean metal surfaces are joined without heat or filler material.
- Pulse welding is a type of welding that uses an electric current to create a spark that melts the metals being joined together.
- Cold welding is typically used for joining metals with a low melting point, such as aluminium or copper.
- Pulse welding can join metals with a higher melting point, such as steel or stainless steel.
- Cold welding is considered stronger than pulse welding due to the lack of filler material and the absence of heat-affected zones.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cold and pulse welding are different welding processes used in industrial applications. Cold welding is best used for non-ferrous metals and where high conductivity is required. Pulse welding is ideal for several types of metal and surfaces and produces high-quality welds requiring less energy. Understanding the differences between these two processes is essential in selecting the right welding process for your particular application.
Rachana is a dedicated and ambitious young woman who has made a name for herself in the metal industry. From her earliest days in the industry, Rachana showed a natural talent for problem-solving and a keen eye for detail. In her free time, She enjoys reading up on the latest advancements in the industry, as well as exploring new ways to innovate and improve upon existing processes.