If you’re in the process of choosing a manufacturing technique for your project, one of the most common questions that come up is whether to use die casting or injection moulding. Both processes are widely used and can produce high-quality parts and components in a wide variety of materials. In this blog post, we’ll take a look at how these two techniques differ and their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Die Casting Process
In the die-casting process, molten metal is injected into a steel die under high pressure. This results in parts and components with high dimensional accuracy and repeatability. The excess material is then removed through ejector pins or by other means, depending on the shape of the part being produced. Die castings are typically created from non-ferrous metals such as aluminum alloys, zinc alloys, copper alloys, magnesium alloys, lead alloys, and tin alloys.
Advantages of Die Casting
One advantage to die casting is that it creates parts with excellent surface finish due to the smoothness of the steel dies used. It also produces parts with superior strength since they have been solidified under extreme pressure. Additionally, die castings can be machined to very tight tolerances as well as have secondary operations performed on them, such as polishing or painting for aesthetic purposes. Finally, because of its fast production rate, die casting is often more cost-effective than other manufacturing processes for producing large quantities of parts or components.
Injection Molding Process
Injection moulding uses thermoplastics instead of metal to create parts or components with complex shapes and sizes. The process involves melting plastic pellets in an extruder before injecting them into a heated cavity within an injection mould tool. Once cooled down, they are ejected from the mould tool by ejector pins so that they can be further processed if necessary (such as painting). Injection moulded products are usually made from polymers such as ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), nylon (Polyamide), polystyrene (PS) or polypropylene (PP).
Advantages of Injection Molding
One advantage of injection moulding is that it produces consistent parts with little variation in quality due to its highly automated nature and tight control over material temperature during production. Additionally, it generally requires less secondary finishing compared to other manufacturing processes like machining, which saves time and money on labour costs. Lastly, injection moulded plastics are lightweight yet strong, which makes them ideal for certain applications where weight may be a factor, such as automotive or aerospace applications where every ounce counts!
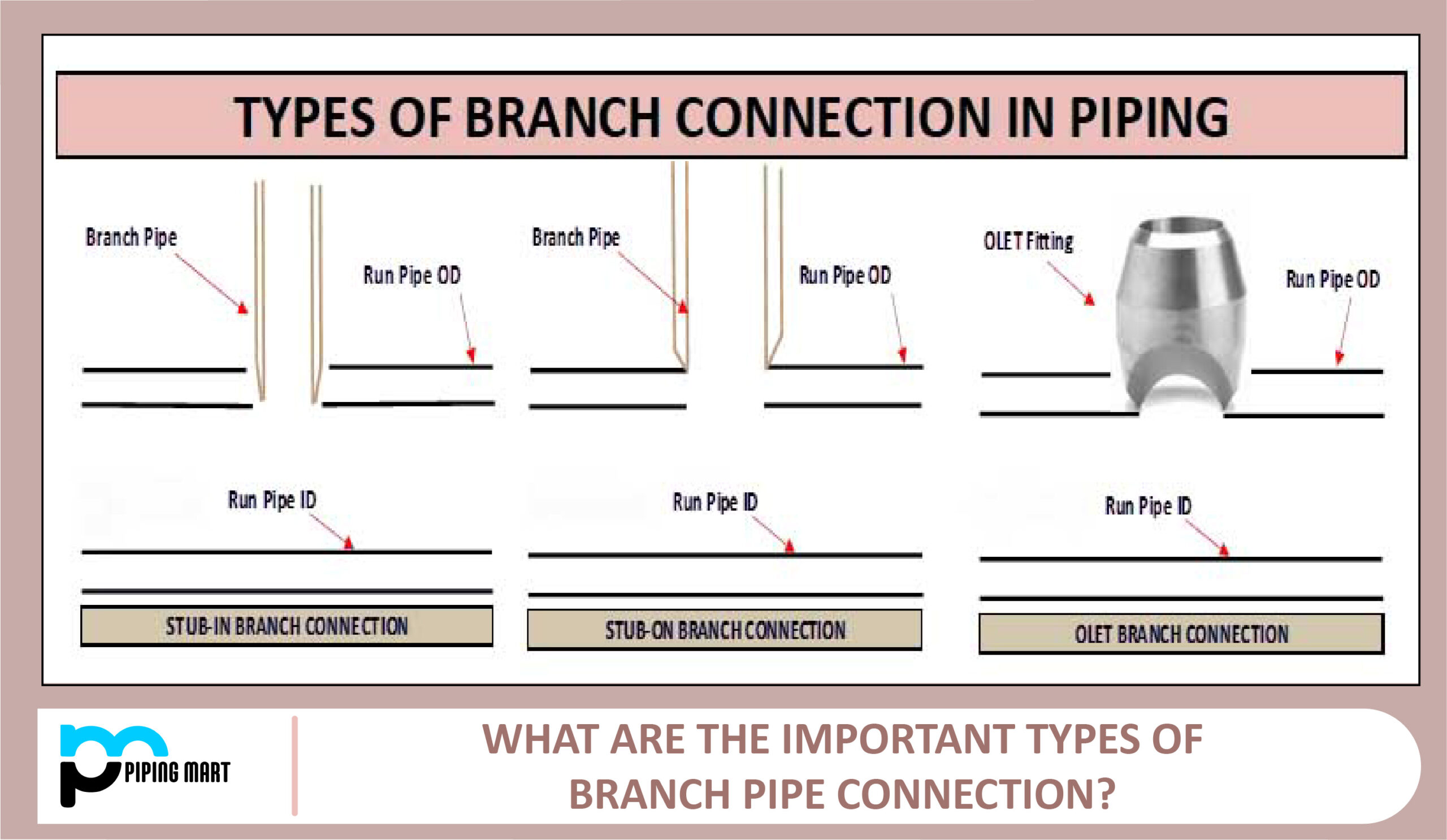
Difference Between Die Casting and Injection Molding
- Die casting is a process that involves injecting molten metal into a mould.
- Injection moulding is a process that involves injecting molten plastic into a mould.
- Die casting is typically used for metals, while injection moulding is typically used for plastics.
- Die casting can produce stronger and more detailed parts than injection moulding.
- Injection moulding is typically faster and less expensive than die casting.
Conclusion:
Die Casting vs Injection Molding – what’s right for your project? Ultimately, it comes down to understanding your needs when determining which manufacturing technique is best for you – both offer advantages depending on what type of product you’re looking to create! For example, if you need precision parts quickly, then die casting would be better than injection moulding since it has faster cycle times, but if you need complex shapes, then injection moulding might be better suited for your needs since it can create intricate designs easily without sacrificing strength or durability. Ultimately there is no “right answer” – just make sure you do your research before deciding which option works best for your project!

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.