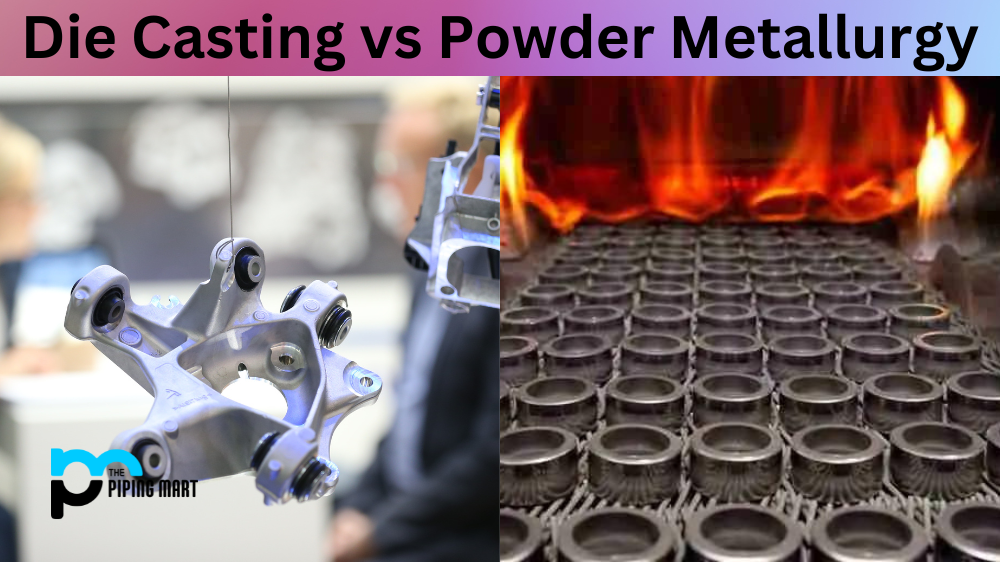
One of the most important decisions any engineer or product designer has to make is what kind of materials and production process to use for a given project. Two popular options are die casting and powder metallurgy. Each has its own advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Let’s look at the differences between these two production processes so you can decide which is right for your project.
Die Casting
Die casting is a production process that uses high pressure to inject molten metal into moulds in order to create components with precise dimensions. The molten metal is injected into the mould under tremendous pressure, which helps ensure that it fills all the intricacies of the mould and results in an accurate, repeatable part. This process is often used for projects where complex shapes are required, as well as when high levels of accuracy are needed.
However, die casting can be expensive due to the cost of machinery and tools required to produce parts in this way. It also requires long lead times as many setups are involved before production begins. Lastly, die casting can only be used with certain types of metals such as aluminium, zinc, copper, or brass — so if your project calls for something else, then you won’t be able to use this method.
Powder Metallurgy
Powder metallurgy (PM) involves combining powdered metals with other additives, such as lubricants or bonding agents, in order to form components with specific characteristics and properties. This method produces parts faster than traditional machining methods since there’s no need for cutting or shaping individual pieces by hand. The PM also allows for greater design flexibility since it can accommodate complex shapes with ease — something that would be difficult or impossible using traditional machining methods like milling or turning. Additionally, PM does not require long lead times as die casting does; it’s possible to produce parts quickly once the design is finalized.
Die Casting vs Powder Metallurgy – What’s the Difference
- Die casting is a process that involves injecting molten metal into a mould to create a desired shape.
- Powder metallurgy is a process that involves mixing metal powder with binders and other materials to create a desired shape.
- Die casting is typically used for high-volume production, while powder metallurgy is typically used for low-volume production.
- Die casting typically has a higher production cost than powder metallurgy.
- Die castings are typically stronger and more precise than powder metallurgy parts.
- Powder metallurgy parts typically have better wear resistance than die castings.
Conclusion:
The decision between die casting and powder metallurgy ultimately depends on what type of materials you will be using, how complex your designs are, how quickly you need your parts produced, and how much you are willing to spend on manufacturing costs. Both processes have their own unique set of strengths and weaknesses that should be taken into consideration when making your decision on which one is best suited for your project needs. A good rule of thumb is to always weigh all options before making a final choice — but whatever you choose will depend entirely on what kind of end result you need from your production process!

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.