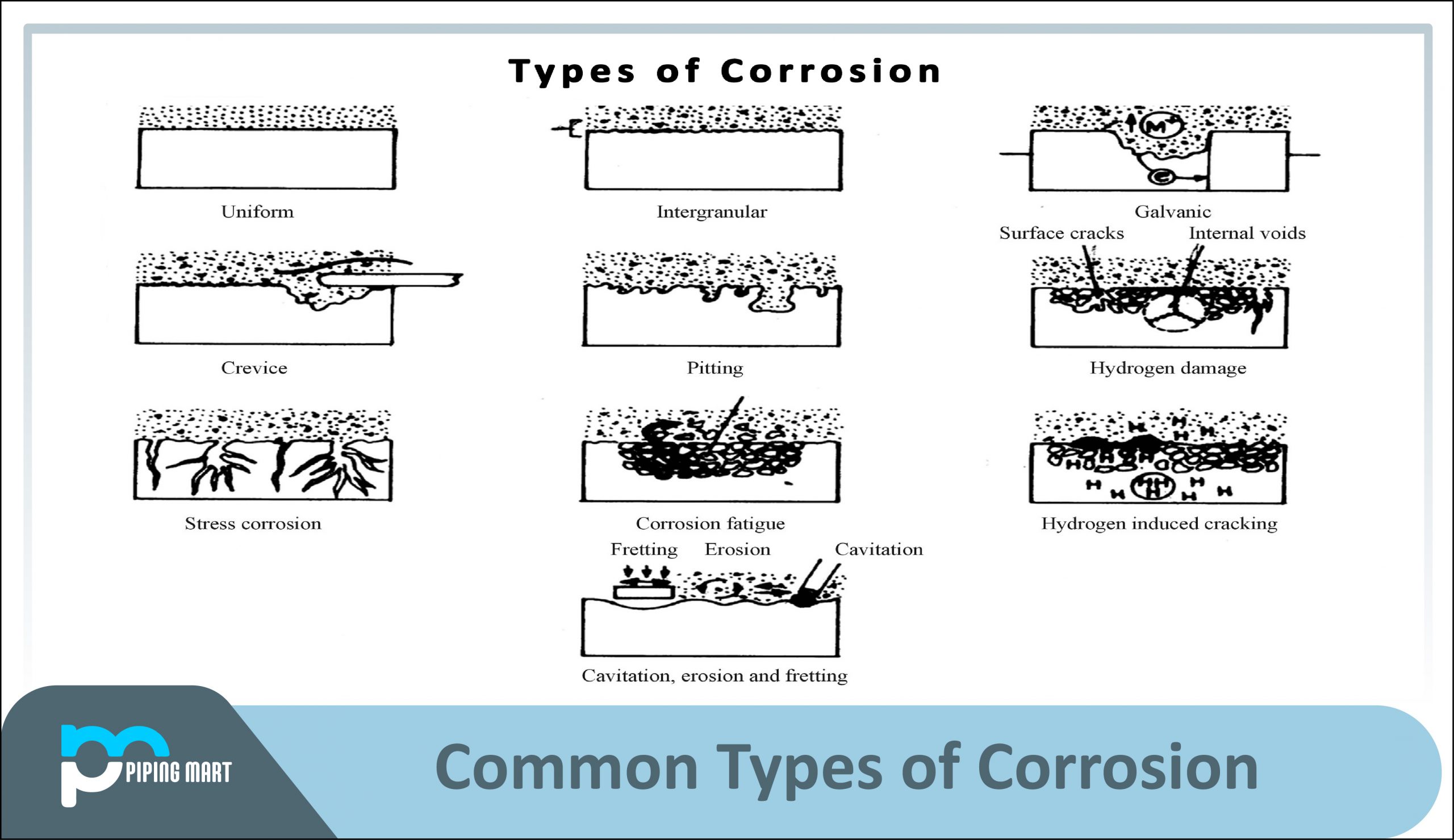
What Is Extrusion?
The extrusion process is used to create objects with a fixed cross-sectional profile. A die made of hot work tool steel is machined with a desired hollow or solid profile. After that, a heated aluminum billet is forced through the die in an extrusion press, resulting in a linear piece of aluminum in the shape of the profile cross-section.
One of the many advantages of the extrusion process is its flexibility, which allows for a wide range of shapes. Manufacturers can also work with brittle materials because the only forces applied to the workpiece are compressive and shear stresses.
Although similar, extrusion should not be confused with drawing, which differs in that the material is pulled rather than pushed through the die, limiting the process to simpler shapes than extrusion. An extrusion can theoretically be infinitely long if you have enough material to push through. Extrusions are typically limited in length based on how they will be transported.
What Is A Seamless Extrusion?
Seamless extrusion is one of the most common methods of extrusion. This entails a fully extruded hollow tube with no welding or bracketing running the entire length of the profile. The process of producing a seamless aluminum tube is known as piercing extrusion. Starting with a solid round aluminum billet as raw material, it is heated to the desired temperature before being punched with a small hole at one end to serve as the starting point.
The main advantage of the seamless extrusion process is the lack of a welded seam, which is the mechanically weakest point of the profile’s structure. As a result, the finished product has greater structural integrity and is more resistant to failures along weld lines; seamless extrusions are the preferred material for pressure vessels. A seamless tube is also ideal for anodizing and other finishing procedures.
What Is Structural Extrusion?
A structural extrusion, as opposed to a seamless extrusion, is intended to be joined to another extruded part via welding, a bracket, or some other type of fastener. This means that, no matter how strong the extruded material is, the weld point or connector holding the pieces together will be the weak point of the extrusion.
A porthole or bridge die method is used to form hollow-profile structural extrusions such as tubes. The aluminum billet is forced through the die with tremendous force at high temperatures, similar to a seamless extrusion. Because the profile wall will separate during the extrusion process, it must be repressed within the die. This will happen while the material is being extruded through the extrusion die in the extrusion press.
Extruded pipes can be distinguished from seamless products by the presence of a visible seam separate from any die lines if the pipe has been finished or anodized.
One of the benefits of extrusion is better control of the eccentricity of the wall thickness. Multi-hole dies, which allow for smaller profile sizes, can also be used. Structural extrusions are also more cost-effective and faster to manufacture.
There are numerous ways to connect structural extrusions, including t-slots, angles, tracks, fasteners, and brackets. Aluminum frames can be used to attach panels, wire mesh, or screens. The industry has progressed to the point where these extrusions can be purchased in kits and quickly assembled. Typical use cases can be found in the manufacturing, retail, automotive, and medical industries. Office workstations, machine bases, enclosures, industrial racking, fixtures, safety guards, stairs, platforms, and material handling carts are examples of applications.

Pipingmart is B2B portal specializes in industrial, metal and piping products. Also, share latest information and news related to products, materials and different types grades to help business dealing in this industry.