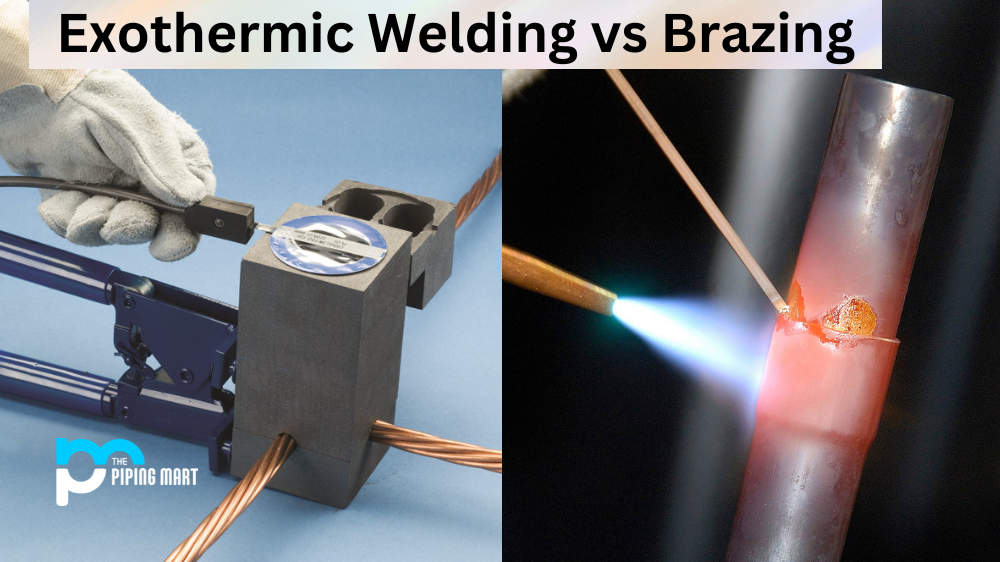
When it comes to metal welding, there is a myriad of options available to welders, each with its own unique benefits. Two popular welding methods are exothermic welding and brazing. Although these two processes have similarities in how they work, they also have a few important differences. Let’s take a closer look at each process.
Exothermic Welding
Exothermic welding is an effective way of joining conductors made from copper or aluminum. In this process, heat is generated through chemical reactions rather than physical means such as burning or heating with a flame or torch. This type of welding is often used for joining cables together because it offers superior strength compared to other types of welding processes. The exothermic reaction causes the metals to melt together, creating an extremely strong bond. The result is an electrical connection that will last for years without deteriorating or needing repairs due to corrosion or wear and tear. It’s also incredibly fast; the entire process can be completed in just a few seconds. Exothermic welding is a type of welding that uses heat to join two pieces of metal together. The process is also known as thermite welding or chemical welding. Exothermic welding is typically used to join metals that are difficult to weld using traditional methods, such as aluminium.
Brazing
Brazing involves using a filler metal to join two pieces of metal together by melting it into the joint between them. The filler metal—often made from brass, bronze, or silver alloys—is melted using a torch, which then flows into the joint before cooling and solidifying once again. Unlike exothermic welding, brazing does not require any chemical reactions; instead, it relies solely on the application of heat energy to melt the filler metal so that it binds with the base materials being joined together. This makes brazing an excellent choice for making complex shapes and intricate designs which would otherwise be difficult, if not impossible, with exothermic welding techniques. However, brazed joints are weaker than those created with exothermic welds as there is no chemical reaction involved in their creation. They can also be more prone to corrosion over time due to the presence of exposed filler material in the joint itself, which can act as points of weakness in extreme environments like saltwater applications. Brazing is a type of welding that uses a filler metal to join two pieces of metal together. The filler metal has a lower melting point than the base metals being joined, so it melts and flows into the joint between the two pieces of metal. Brazing is typically used to join metals that are difficult to weld using traditional methods, such as stainless steel.
Difference Between Exothermic Welding vs Brazing
Advantages of Exothermic Welding
One advantage of exothermic welding is that it can be used to join metals that are difficult to weld using traditional methods, such as aluminium. Additionally, exothermic welding is typically faster than other welding methods, and it can be used to weld large joints in one pass.
Advantages of Brazing
One advantage of brazing is that it can be used to join metals that are difficult to weld using traditional methods, such as stainless steel. Additionally, brazing does not require the use of electricity, so it can be used in locations where there is no power source available.
Disadvantages of Exothermic Welding
One disadvantage of exothermic welding is that it can be dangerous if not done properly, as the heat generated by the process can cause burns. Additionally, exothermic welding produces fumes that can be harmful if inhaled, so proper ventilation must be used when performing the process.
Disadvantages of Brazing
One disadvantage of brazing is that it requires the use of a filler metal, which can add cost to the process. Additionally, brazing can be time-consuming if multiple passes are required to fill the joint completely.
Conclusion:
Both exothermic welding and brazing offer advantages for welders depending on their intended application and desired outcome result; however, there are some key differences between these two processes that make one better suited for certain jobs than others. Exothermic welding is stronger than brazing but requires a chemical reaction in order to create a bond between conductors while brazing relies only on heat energy from an external source such as a torch in order to create its joints which makes it far less durable when compared with exothermically welded joints but able to produce more intricate results than its counterpart due primarily to its reliance on manual manipulation during the filling process itself rather than relying heavily upon automated machinery like what may be required when performing an exothermically welded joint correctly every time without fail. Ultimately, it’s up to you as the welder/metalworker as well as your client’s needs/desires, when deciding which method works best for your particular project!

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.