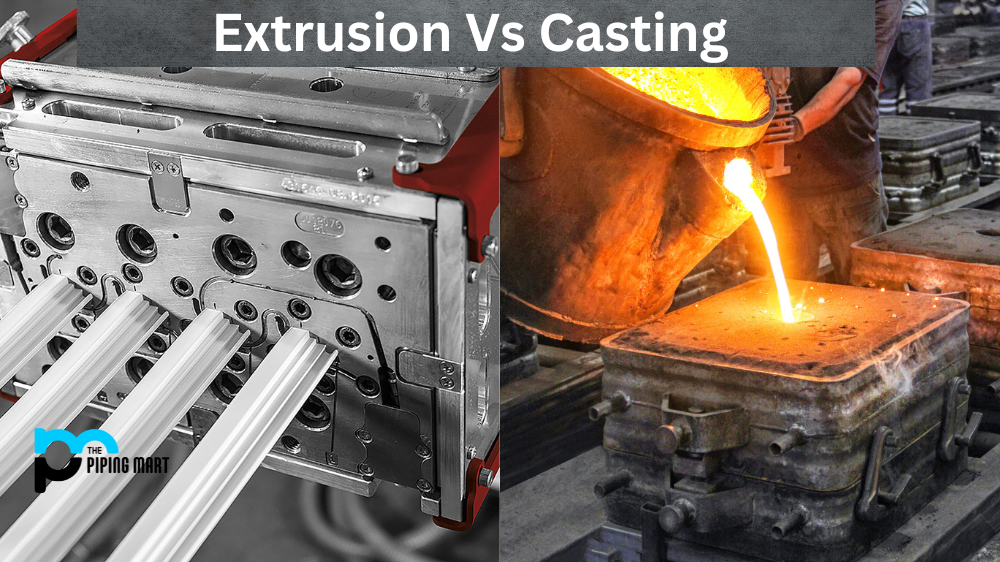
If you’re in the manufacturing industry, you’re probably familiar with both extrusion and casting. These two processes are often confused, but they produce very different results. Let’s take a look at how each process works, as well as their advantages and disadvantages.
What is Extrusion?
Extrusion is a manufacturing process where a material—such as metal, plastic, or rubber—is heated until it reaches a malleable state. The material is then forced through an opening by use of pressure, resulting in a product with a consistent cross-section. The extruded product can be solid or hollow, depending on the shape of the die used to create it. In addition to metals and plastics, extrusion can also be used for food production (e.g., macaroni) and even medical applications (e.g., catheters).
Extrusion Advantages and Disadvantages
The primary advantage of extrusion is that it produces consistent shapes with minimal waste materials. This makes it ideal for producing parts that have standard dimensions or need to fit together in specific ways (e.g., pipes). Additionally, since the process itself is relatively simple and quick, it is usually less expensive than other manufacturing processes, such as casting or forging. However, there are some drawbacks to extrusion—namely, its limited range of shapes and sizes that can be produced and its reliance on dies which must be frequently replaced due to wear and tear over time.
What is Casting?
Casting is another method used for producing parts from metals or plastics. Unlike extrusion, casting involves pouring molten material into a mold and allowing it to cool before being removed from the mold for finishing work. The molds used in casting can be made from sand or plaster of Paris mixtures; however, more complex molds may require specialized materials such as ceramics or waxes in order to produce intricate shapes or patterns on the finished part.
Casting Advantages & Disadvantages
The main advantage of casting is its versatility; almost any shape imaginable can be produced using this method with relative ease compared to other manufacturing processes, such as machining or stamping. Additionally, because no pressure is applied during the process itself, there are fewer chances for defects in the final product than there would be with extrusion or other methods involving direct force/pressure on the material being worked with. On the downside, however, casting requires more time than other methods due to its complexity; additionally, there are usually more waste materials produced in comparison with simpler processes like stamping or machining due to excess material needed for making moulds/cores etc.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both extrusion and casting have their own unique advantages and disadvantages depending on what type of part you need to be created from what type of material, understanding how each process works will help you make an informed decision when selecting one over the other for your project needs! Both processes offer unique benefits that should not be overlooked when considering which one best suits your requirements! Thanks for reading!

Pipingmart is a B2B portal that specializes in metal, industrial and piping items. Additionally, we share the latest information and information about materials, products and various types of grades to assist businesses that are involved in this business.