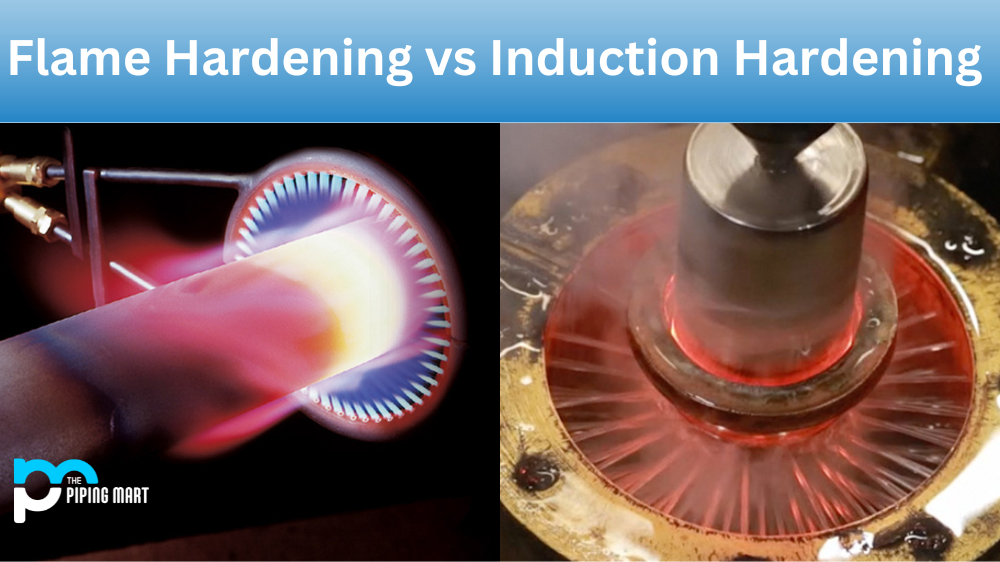
You’ve probably heard of flame hardening and induction hardening if you’re in the hardening business. However, do you know what each of these processes entails? Do you understand the differences between them? Let’s look at flame hardening vs induction hardening to help you decide which process best suits your needs.
Flame Hardening
Flame-hardening is a process used to harden metal surfaces. It uses a flame to heat the material’s surface to be hardened and then quenching it with water or oil. The result is an incredibly tough metal surface that can withstand more wear and tear than an untreated surface. Flame-hardened metals are less likely to corrode or break down over time due to their increased hardness.
The downside of flame-hardening is that it requires high temperatures and can cause warping or distortion if not done properly. For this reason, working with experienced professionals who understand how to control the flames and apply the cooling agent correctly to avoid warping or distortion problems is important. Furthermore, flame-hardened metals may be slightly harder than those treated with induction hardening and more brittle, making them more susceptible to cracking under pressure.
Induction Hardening
Induction hardening is similar to flame hardening in that it uses heat to increase the hardness of a material’s surface; however, instead of a flame, induction hardeners use electricity generated by an induction coil placed around the piece being hardened. This creates a magnetic field that heats the component through resistance heating without creating open flames or hot spots on its surface. Induction-hardened components are less likely to warp or distort because they don’t require as high temperatures as flame-hardened pieces do — plus, they cool faster thanks to their lack of contact with open flames or hot spots on their surfaces. Additionally, induction-hardened pieces tend to be less brittle than those treated with flame-hardening methods because they are heated more evenly throughout their entire surfaces rather than just on specific points like in traditional heat-treating processes such as flame-hardening techniques.
Difference Between Flame Hardening and Induction Hardening
- Flame hardening is a surface hardening process that uses a flame to heat the surface of a workpiece.
- Induction hardening is a surface hardening process that uses an electromagnetic field to heat the surface of a workpiece.
- Flame hardening is typically used on larger workpieces, while induction hardening is typically used on smaller workpieces.
- Flame hardening can be used to harden the entire surface of a workpiece, while induction hardening can be used to selectively harden only certain areas.
- Flame hardening typically produces a more uniform hardness over the entire surface of the workpiece, while induction hardening can produce a more localized hardness.
Conclusion:
When considering whether your project will benefit from flame hardening vs induction hardening, several key factors are at play, such as cost-effectiveness, speed of application and overall durability required for your project completion goals. While both processes have their advantages and disadvantages depending on what you need for your project, understanding these differences will help ensure you make a good decision when selecting which method best suits your needs for optimal results!

Pipingmart is a B2B portal that specializes in metal, industrial and piping items. Additionally, we share the latest information and information about materials, products and various types of grades to assist businesses that are involved in this business.