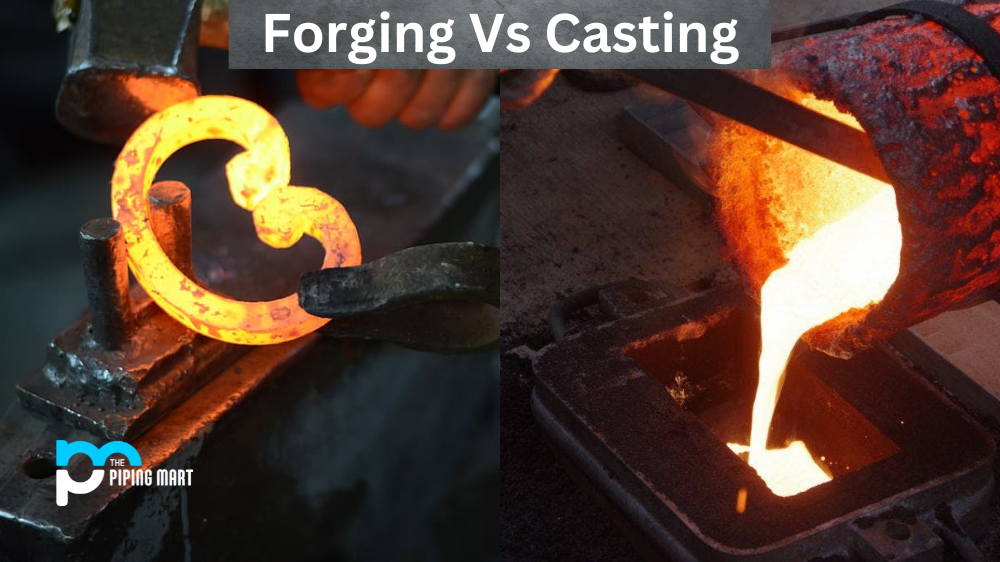
Have you ever wondered what the difference is between forging and casting? Many people don’t really know or understand the difference. In this blog post, we will explain what each one is and why it matters for your project.
What is Forging?
Forging is a process of creating metal parts by applying compressive force. The metal is heated to a certain temperature before shape alteration begins. This allows the metal to become malleable enough to be formed into various shapes when pressure is applied with hammers or presses. It can also be formed under extreme temperatures and pressures in an autoclave. The forging process creates parts that have improved strength, durability, and fatigue resistance because of their grain flow properties which are formed during the deformation process, which aligns the grains in one direction.
Forging can create intricate shapes that would be impossible to manufacture with other methods. Parts produced by forging are often stronger than those created through other processes, such as machining or welding.
What is Casting?
Casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mould cavity, where it solidifies once cooled down and takes on the shape of the cavity walls. Molten metals are injected into a pre-made mould using gravity or pressure-assisted techniques. The casting process enables complex internal geometries due to its ability to form cavities within thicker sections of material without any additional machining required from outside sources. Because of this feature, castings often require fewer secondary operations (such as assembly, finishing, etc.) compared to forgings or machined components. Additionally, castings can have greater part complexity than forged components because they do not need to be formed from a single piece; multiple pieces can be combined in order to create complex shapes that would otherwise be too difficult or too expensive to create via other manufacturing processes.
The casting process produces parts with good surface finish characteristics and close tolerances compared to forgings which typically require additional finishing operations such as grinding and polishing in order to meet tight dimensional requirements.
Difference Between Forging and Casting
Forging
Forging is a manufacturing process in which metal is heated and then shaped using hammers or presses. The advantage of forging over other manufacturing processes is that it can produce parts with very high strength. Additionally, forging can be used to create parts with complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using other methods.
Casting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which metal is melted and then poured into a mould. The advantage of casting over other manufacturing processes is that it can produce parts with very intricate designs. Additionally, Casting can be used to create parts with very smooth surfaces.
Cost
Forging is typically more expensive than Casting, as it requires more specialized equipment and labour. However, the cost of each individual part may be lower for forgings when compared to castings, as forgings do not require the use of moulds.
Lead Time
The lead time for forgings is typically longer than the lead time for castings, as forgings require more time to heat and shape the metal. However, the lead time for each individual part may be shorter for forgings when compared to castings, as multiple parts can be produced at the same time using forging methods.
Strength
Forgings typically have higher strength than castings, as the metal is compressed during the forging process, which increases its density. Additionally, forgings typically have superior fatigue resistance when compared to castings, as the grain structure of the metal is aligned during the forging process.
Conclusion:
Forging vs Casting – which one should you choose for your project? That depends on several factors such as cost, time frame/deadline, the complexity of design, quantity needed etc., but ultimately it comes down to what best suits your needs and requirements for your specific job/project at hand. If you need a part with high strength and fatigue resistance, then forging might be your best bet, whereas if you need complex internal geometries or high surface finish characteristics, then Casting might be more suitable for you! Ultimately both processes have their advantages and disadvantages, so consult an experienced engineer who can help guide you towards making the best decision possible for your particular application! With that said, we hope this article has been helpful in providing some insight into these two processes so that you can make an informed decision when choosing between them!

Pipingmart is a B2B portal that specializes in metal, industrial and piping items. Additionally, we share the latest information and information about materials, products and various types of grades to assist businesses that are involved in this business.