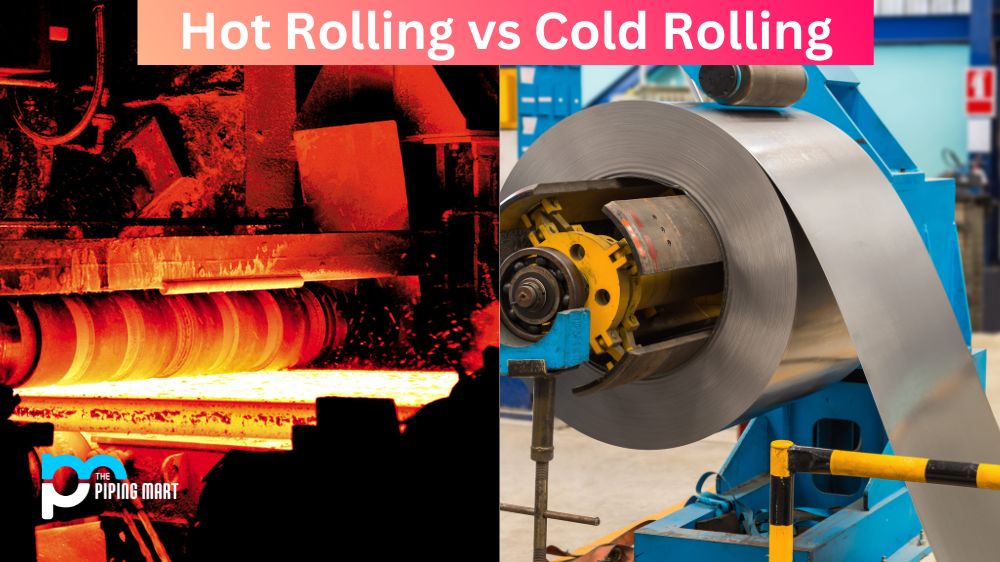
Hot rolling and cold rolling are two different methods of shaping metal for manufacturing. Both techniques involve a combination of pressure and heat to create the desired shape, but the major difference lies in the temperature of the metal being worked on. While hot rolling is done at temperatures above recrystallization, cold rolling is done at cooler temperatures, resulting in a much smoother finish. Let’s take a closer look at how these two methods differ.
Hot Rolling
Hot rolling is a metalworking process that occurs above the material’s recrystallization temperature (usually between 1700-750 degrees Fahrenheit). This technique is used to make large parts such as railroad tracks, I-beams, pipes and tubes, which require strong structural integrity. During this process, heated materials are passed between two rollers to reduce their thickness. The pressure applied during this process causes plastic deformation that forms flat surfaces on both sides of the part being processed. As hot-rolled steel cools down, it shrinks slightly due to thermal contraction and its strength increases due to strain hardening.
Cold Rolling
Cold rolling is a metalworking process that takes place below the material’s recrystallization temperature (usually around room temperature). This method uses rolls or lubricated dies in order to shape materials such as brass, aluminium alloys and stainless steel into thin sheets or rods with a smooth finish. Cold rolling applies greater amounts of pressure than hot rolling—up to 40 tons per square inch compared to 20 tons per square inch in hot rolling—so it can be used to make very thin parts with high precision and accuracy. Cold-rolled parts also have improved surface finishes because they don’t suffer from scale formation as hot-rolled parts do.
Difference Between Hot Rolling and Cold Rolling
- Hot rolling is a process that occurs at high temperatures above the recrystallization temperature of the material.
- Cold rolling is a process that occurs at low temperatures below the recrystallization temperature of the material.
- Hot-rolled products have a rougher surface texture than cold-rolled products.
- Hot-rolled products are typically less precise than cold-rolled products due to the higher temperatures used during hot rolling.
- Hot rolling is typically used to create large-scale products, while cold rolling is used to create smaller-scale products.
- Hot-rolled products are more likely to experience scale formation than cold-rolled products.
Conclusion:
Hot rolling and cold rolling are two different processes used for shaping metals into various forms for manufacturing purposes. Hot rolling is done at temperatures above recrystallization, while cold rolling is done at room temperatures or cooler temperatures, depending on the type of material being rolled out. Hot-rolled materials are typically stronger than those made through cold-rolling processes due to strain hardening effects created by applying pressure during processing; on the other hand, cold-rolled materials tend to have smoother surfaces because they are not subject to scale formation like hot-rolled materials are. When deciding which process best suits your needs, consider factors such as cost efficiency and desired product quality before making your choice!

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.