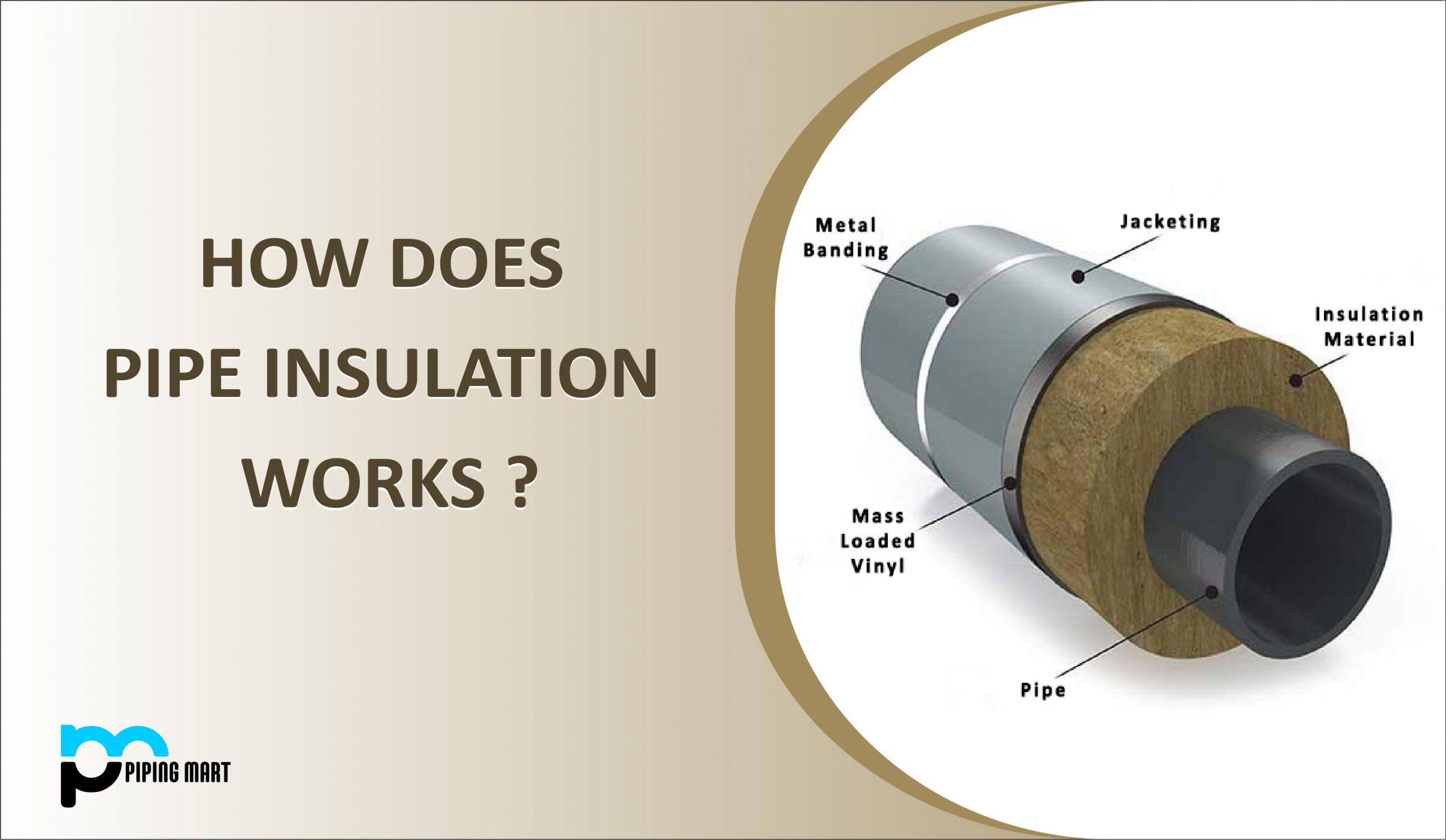
When a material or combination of materials is wrapped around a pipe to slow down the flow of heat energy, it is called pipe insulation. As a result, pipe insulation helps in reducing energy losses and minimizing energy costs. The piping must be insulated in accordance with the insulation class, operating temperature, and insulation thickness.
What purpose does pipe insulation serve?
A piping insulation system has three primary functions:
- Heat Conservation – The substantial reduction in the heat energy transfer from the pipe system’s surface. As a result, pipe insulation helps to save energy.
- Cold Insulation – The prohibition of moisture development and accumulation on the pipe system’s surface due to frost on cold surfaces.
- Personal Protection – Preventing potentially hazardous human contact with the exposed pipe system’s surface.
Furthermore, there are also other merits to pipe insulation, which are noted below.
- Piping insulation contributes to improvements in process temperature regulation.
- Preventing vapor flow and accumulation on cold surfaces.
- Increase thermal efficiency, power generation, and process system efficiency.
- Reduce serious pipe damage in fire hazards or dangerous occurrences.
- Significantly reduce air pollution emissions.
- Depending on the process, steam traced or electric traced insulation, regeneration insulation, jacketing, and so on may be used.
- Fire control, fire protection, and sound insulation to absorb vibration are supplied as per the project specifications or ITB standards.
How many types of pipe insulation are there?
- Hot Insulation
To restrict the flow of energy from the flow of fluids, on hot surfaces of the piping system, hot insulation is applied. As a result, the primary goal of hot pipe insulation is thermal conservation. Mineral wool, glass wool, calcium silicate, and other similar materials are commonly utilized as hot insulating materials.
- Cold Insulation
On cold surfaces of the piping system Cold insulation is applied to prevent heat gain from the outside or to avoid condensation. Cold insulating materials that are commonly utilized include polyurethane foam, expanded perlite foam, expanded polystyrene foam, and others.
- Fibrous Insulation
Fibrous insulation is made up of small-diameter fibers that separate the air space finely. The fibers can run parallel or perpendicular to the surface being insulated, and they can be connected or not.
Silica, slag wool, rock wool, and alumina-silica are common fibers used in pipe insulation. Glass fiber and mineral wool are the two most commonly utilized pipe insulations of this sort. For structural integrity, their fibers are typically bound using organic binders.
- Personal Protection Insulation
To avoid individual thermal injuries, personal protection insulation is supplied. Personal protection insulation is installed on any exposed piping surfaces that exceed 65 degrees Celsius. Areas that are inaccessible to construction or maintenance workers can be exposed to heat. Personal protection insulating materials include an open mesh metal guard, mineral wool, and others.
Personal protection necessitates that exposed surfaces within 2100 mm vertically or 600 mm horizontally of normal access, walkway, or work area be insulated.
- Acoustic insulation
Acoustic insulation is installed on all pipework that is thought to be a possible sound source. The primary goal is to keep the vibration noise at an appropriate level. Acoustic insulation typically has a minimum thickness of 75 mm. Acoustic insulation materials include Acoustic Foam, fiberglass, polyester or polyurethane foams, rock wool, mass-loaded vinyl, and others.
- Cellular Insulation
Cellular pipe insulation material is composed of smaller individual cells that are separated from one another. Glass or foamed plastics like cellular glass, phenolic foam, or nitrile rubber are basic cellular materials used as pipe insulation.
- Granular Insulation
Granular insulation is made up of small granules with gaps or void spaces. Because gas can move between separate spaces, it is not regarded as real cellular material. This type is produced as a loose or pourable material, or in combination with a binder and fibers. They may go through a chemical reaction to generate stiff insulation. These types of insulation include calcium silicate and vermiculite.

Pipingmart is B2B portal specializes in industrial, metal and piping products. Also, share latest information and news related to products, materials and different types grades to help business dealing in this industry.