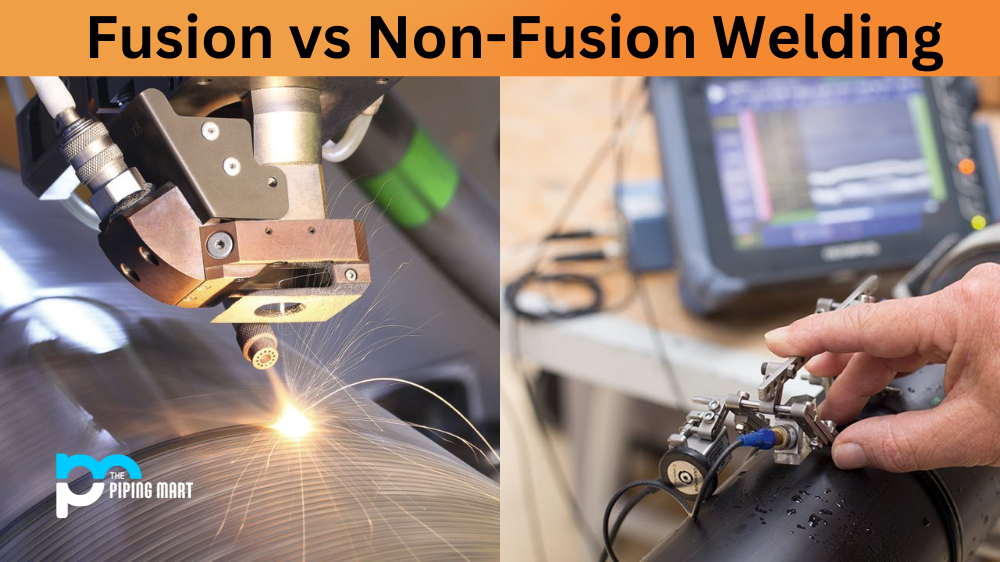
Welding is an incredibly important skill in many industries, such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive repair. It’s a complex process that requires specialized tools and techniques to ensure the welds are strong and reliable. One of the key distinctions in welding is between fusion and non-fusion welding. Let’s take a closer look at what sets these two types of welding apart from each other.
Fusion Welding
Fusion welding is the most common type of welding used today. The heat generated by fusion welding melts both the base metal (the material being welded) and the filler metal together, creating a single piece with a solid bond between them. This type of welding uses temperature extremes to melt the metal rather than pressure or force. There are several different methods for performing fusion welding, including oxy-fuel, arc, spot, inert tungsten gas (TIG), and inert metal gas (MIG). These various methods involve using high temperatures created by an electric current or a fuel source such as acetylene or propane in order to melt the metals together.
Non-Fusion Welding
Non-fusion welding does not use temperature to join materials together; instead, it relies on pressure or force to bind them together into a cohesive unit. Examples of non-fusion welding include riveting, brazing, soldering, staking, clinching, adhesive bonding and mechanical fastening. Non-fusion processes require skilful application because there must be enough force applied to create a strong bond without causing damage to either metal piece being joined together. While non-fusion processes are often simpler and require less equipment than their fusion counterparts, they can sometimes lack strength when compared with fusion welds which creates an additional consideration for those looking to choose between them for any given project.
Difference Between Fusion and Non-Fusion Welding
- In fusion welding, the two pieces of metal to be joined are heated until they melt.
- In non-fusion welding, the two pieces of metal to be joined are not heated until they melt.
- Fusion welding is more likely to result in a stronger joint than non-fusion welding.
- Fusion welding is more likely to result in a joint that is less likely to leak than non-fusion welding.
- Fusion welding is more expensive than non-fusion welding.
- Fusion welding is more time-consuming than non-fusion welding.
Conclusion:
When it comes time to decide which type of welding is best suited for your needs, it’s important to weigh all factors carefully before making a decision. Fusion welds are usually stronger but require special equipment, while non-fusion processes may be faster but lack some strength when compared with their fusion counterparts. Ultimately each situation is unique, so it’s important to understand how each process works so you can make an informed decision about which one will provide you with the best results for your particular project! With this knowledge in hand you can make an informed decision about when and where each type of welding should be used for maximum effectiveness!

A passionate metal industry expert and blogger. With over 5 years of experience in the field, Palak brings a wealth of knowledge and insight to her writing. Whether discussing the latest trends in the metal industry or sharing tips, she is dedicated to helping others succeed in the metal industry.