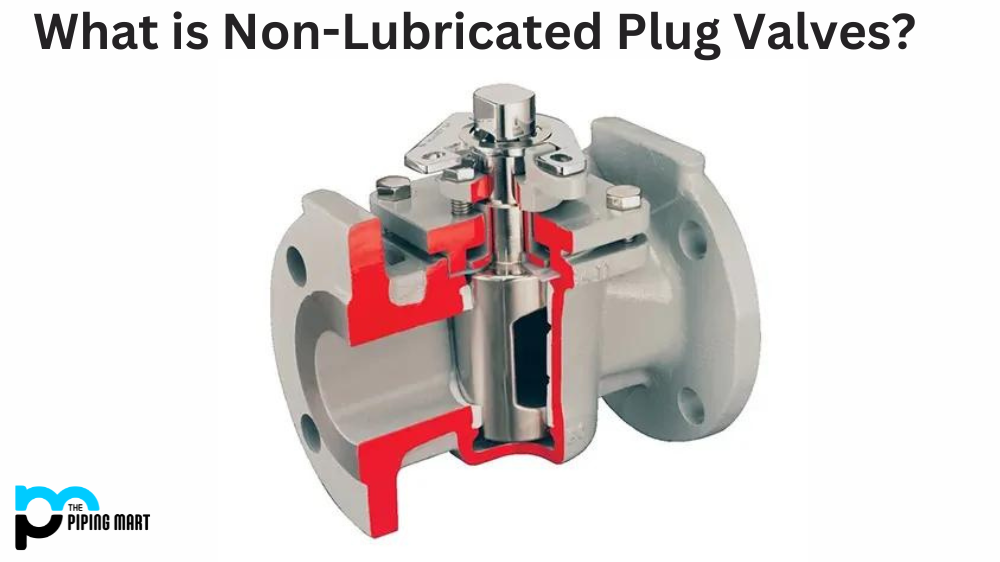
The hardening process is critical for any metal processing project to make it more durable and available for long-term use. However, there are multiple ways to achieve hardening, but oil hardening and air hardening are two commonly used methods. These methods have specific characteristics and advantages depending on the project’s requirements. Therefore, this article discusses these two hardening methods and compares their benefits and drawbacks to help you choose the best one for your project.
Oil Hardening
Oil hardening is when the metal is submerged in an oil medium and heated to a specific temperature range. The oil helps to quench the metal by cooling it down quickly, resulting in a rugged and durable surface. The oil’s composition is vital in this process, as different types of oil give different hardening results.
On the other hand, oil hardening can cause distortion and cracking in small parts due to the medium’s viscosity. This process is also relatively slow and unsuitable for complex geometry parts. However, it’s ideal for large amounts because oil has an excellent cooling capacity and provides a smoother quenching than water. It’s also better for parts that need to retain some flexibility.
Air Hardening
In the air-hardening process, the heated metal is allowed to cool down naturally in the air. This process quenches the metal’s surface layer and hardens it by keeping it at a high temperature for a specific time. Air hardening is ideal for complex geometries and small parts because it doesn’t have the viscosity and surface tension issues that oil hardening can experience.
Similarly, air hardening is quicker and more energy-efficient compared to oil hardening. However, air hardening is relatively less effective for large parts because controlling the temperature of the metal can be challenging due to the atmosphere’s inconsistency. Air-hardened features can also be less flexible and more brittle than oil-hardened ones.
Difference Between Oil Hardening and Air Hardening
Choosing the Right Method
Choosing the proper hardening method depends on the project’s requirements, mainly its size, complexity, and required hardness level. Oil hardening is generally suitable for more significant parts, thicker cross-sections, and parts that need some flexibility. On the other hand, air hardening is ideal for small and geometrically complex components that must be hard and brittle.
It’s best to consult a metal processing expert to help you choose the suitable method and determine the correct quenching temperatures and the medium’s composition. This will ensure that the hardening process produces the desired results and meets the project’s specifications.
Additional Hardening Techniques
It’s worth noting that hardening isn’t the only technique used to improve metal properties. Additional courses like case hardening, induction hardening, and flame hardening can achieve different metallurgical properties like flexibility, toughness, and wear resistance. These processes can be combined with hardening to produce a metal part that has the desired properties.
Benefits of oil hardening
The benefits of oil hardening include good dimensional stability, meaning that the steel will not distort during heating and cooling. Additionally, oil hardening provides a more uniform hardness throughout the steel than air hardening, which can result in a more rigid surface but a softer core.
Benefits of air hardening
The benefits of air-hardening include less distortion in the steel during the heating and cooling process. Additionally, air hardening can result in a more rigid surface but a softer core, which may be desirable in some applications.
Drawbacks of oil hardening
The drawbacks of oil hardening include that it is a slower process than air hardening and requires special equipment, such as an oil bath. Additionally, oil-hardened steels are more susceptible to corrosion than air-hardened steels.
Drawbacks of air hardening
The drawbacks of air hardening include that it is a faster process than oil hardening and does not require special equipment. Additionally, air-hardened steels are less susceptible to corrosion than oil-hardened steels.
Conclusion
In summary, oil and air hardening are effective ways to harden metals for better properties and longer lifespans. The choice between these two methods depends on the project’s requirements, mainly the part’s size, geometry, and hardness level. While oil hardening is ideal for more significant amounts and provides flexibility, air hardening is perfect for small, complex details with higher hardness levels. Therefore, consulting with an expert in metal processing is essential to determine the proper hardening method, additional techniques, and quenching temperatures. When done right, the hardening process can make the metal more durable, wear-resistant, and long-lasting, making it suitable for various industrial applications.

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.