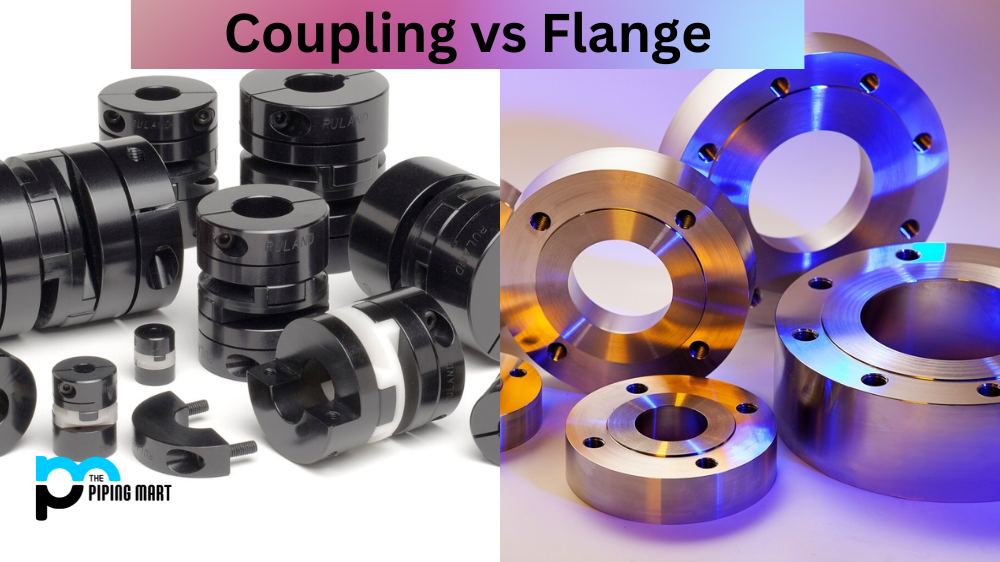
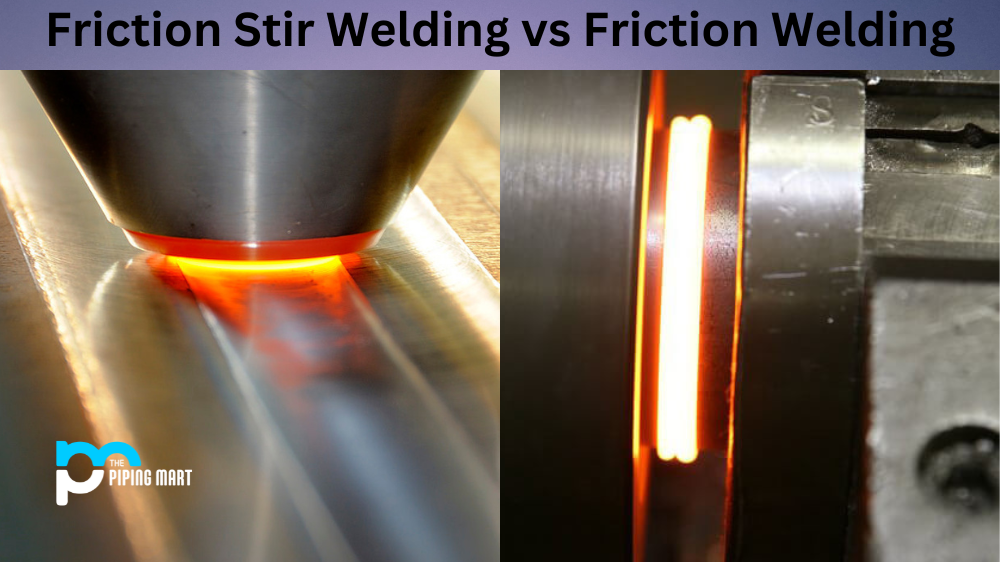
The phrase “positive material identification” (PMI) refers to a technique used in industrial inspection analysis to ascertain the composition of a specific alloy and the components that make up its constituent parts.
Positive material identification (PMI) is a crucial non-destructive testing (NDT) technique used to confirm that materials provided comply with the necessary norms and requirements. PMI is specifically used to verify that the chemical composition of the metallic parts has the right proportion of essential elements, ensuring that material qualities like corrosion resistance satisfy the criteria.
Inspection Methods Used in the Practice of Positive Material Identification (PMI)
- optical emission spectrometry (OES) – The substance is exposed to a spark from an electrode in an argon atmosphere while using the OES method of positive material identification. The spark causes the material to emit light with a distinct hue depending on the makeup of the material. By observing that light, it is possible to determine the component’s chemical makeup.
- Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) – A highly focused laser is utilised to ablate the sample surface in the LIBS, or Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy, method of PMI. A plasma is created when atoms and ions are electrically stimulated. They emit distinctive wavelengths of light, or “unique fingerprints,” as these atoms return to their ground states. Each element that the LIBS analyzer analyses to produce quantitative and qualitative results has a unique set of these “fingerprints.” This is the most recent technology for positive material identification testing.
- X-ray fluorescence (XRF) – X-rays are used in the XRF technique. The component is exposed to the PMI gun’s flux of x-rays. The material’s atoms take in this energy and release secondary x-rays that are particular to the elements in the material. The XRF PMI gun provides the material’s composition by measuring the energy and intensity of the secondary x-rays.
Application of PMI
The necessity of specific materials during the design phase was brought to light by several mishaps in the manufacturing and petroleum sectors. Positive material identification guarantees that the vendor’s material is either exactly the same as requested or differs from it. As a result, the plant’s structural and mechanical integrity is preserved. Because of this, PMI is now a popular inspection tool. The following sectors have found use for positive material identification:
- Oil & Gas, Chemical, Petrochemical, Refinery,
- Aerospace
- Steel
- Power plant
- Pharmaceutical etc
Advantages of PMI
PMI testing is flexible and can be used to any size or shape. It has several benefits, including the following:
- a portable, lightweight tool for accurate material identification testing.
- Produce results that are very repeatable, dependable, and consistent.
- quick assessments of the materials or components.
- On-site PMI technology
- generally requires little advance planning
- for quick PMI, a large materials-data library
- A needed replacement for original materials reports that are lost
- Results with high accuracy for effective quality control.
- field research that meets laboratory standards.
- decreased danger of corporate responsibility.
- rapid auditing times.
Thus, there are many guidelines and standards for PMI, a non-destructive testing technique that is widely used. It make sure all legal and governmental standards are followed. Safety standards that are documented can lower the risk of corporate liability.

Pipingmart is B2B portal specializes in industrial, metal and piping products. Also, share latest information and news related to products, materials and different types grades to help business dealing in this industry.