Have you ever wondered which metal cannot be forged? Many people make the assumption that anything made of metal can be heated and then put into a specific shape. However, this is not always the case – there are some metals out there that simply cannot be forged no matter how much heat or pressure is applied! In this blog post we’ll explore these mysterious metals, how they behave differently from others, and speculate on why they are unable to hold their form when subjected to extreme temperatures or pressure. So if you’re curious about what metallurgy mystery lies beneath our feet every day, read on for more information!
Cast Iron:
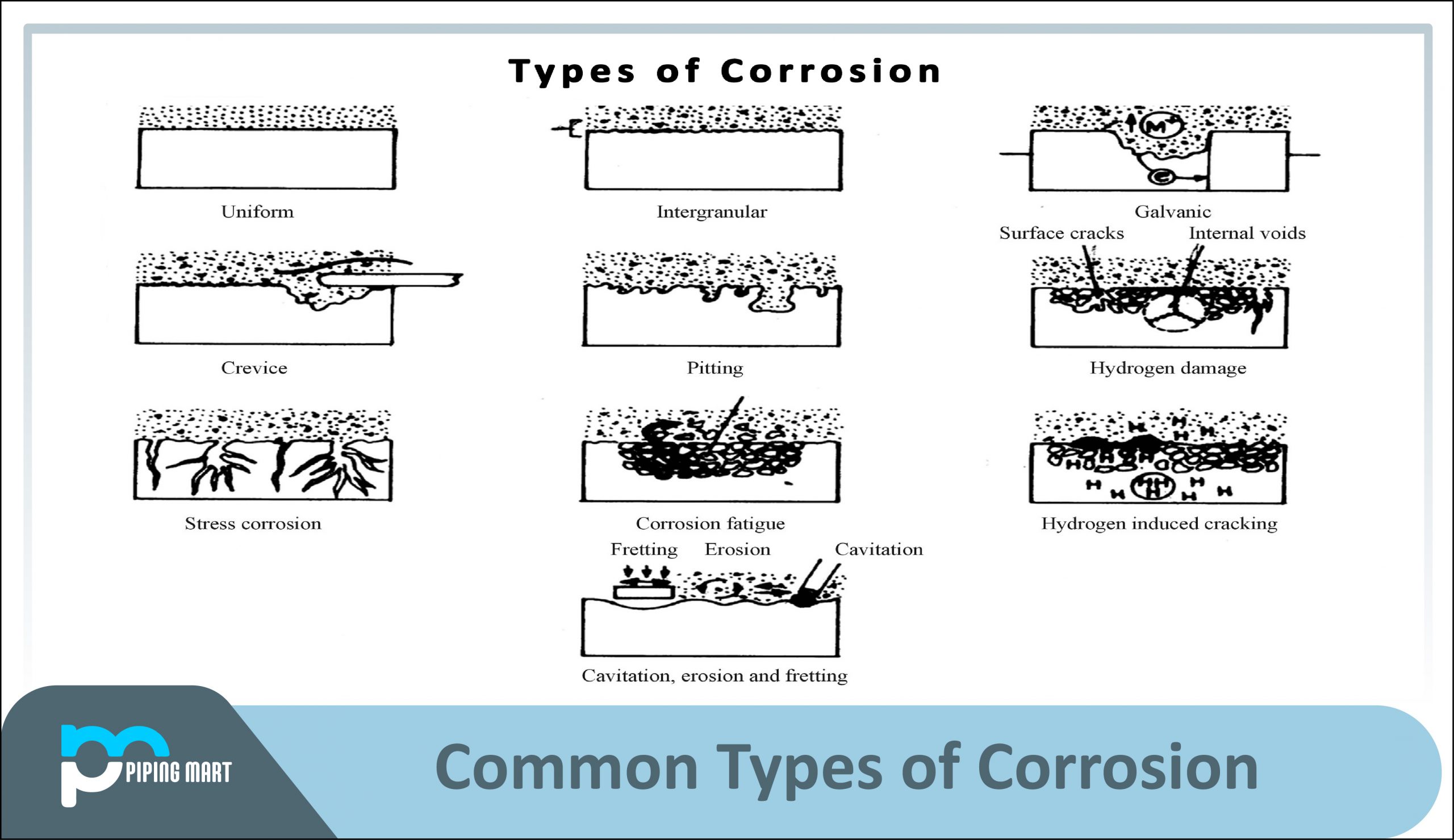
Cast iron is a category of iron-carbon alloys with greater than 2% carbon content. Its use stems from the fact that it melts at a significantly lower temperature. Cast iron’s superior castability is due to the combination of high carbon content and the existence of silicon. White cast iron has carbide impurities, which allow cracks to pass straight through, grey cast iron has graphite, which deflects a passing crack and initiates numerous new cracks as the fracture point, and ductile cast iron has spherical graphite “nodules,” which stop the crack from progressing further.
Mechanical Properties of Cast Iron:
Mechanical characteristics of a material describe how it reacts to various loads and are used to assess its appropriateness for various uses. Organizations like the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) establish specifications so that customers may buy materials with confidence that they will suit their needs. ASTM A48 is the most widely used cast grey iron standard. The welding cast iron holds the pieces together which leads to specifications which leads to crucial. Instead, fractures and failures might occur because the weld does not meet the characteristics of materials that are welded together.
Following of the Properties:
- Hardness– Abrasion and indentation resistance of the material.
- Toughness – Materials strength to get the energy.
- Ductility – To have the strength to change without fracture.
- Elasticity – Ability to get back to the original dimension after it has changed.
- Malleability – Materials’ ability to change under compression without its breaking.
- Tensile Strength– The maximum longitudinal stress that a material can withstand before ripping apart
- Fatigue Strength– The maximum stress that a material can sustain without breaking during a certain number of cycles-
Why it Cannot be Forged?
The carbon percentage of cast iron is around 4.2 wt%, which is the soluble limit of carbon in iron. As a result, while cast iron is resistant to wear, it is very fragile and cannot be forged. You need to have lower the carbon concentration to roughly 2% or less, which implies you’d have steel that could be forged. What methods are used to lower the carbon content in cast iron? By melting it and forcing oxygen through all of it, carbon is removed in the form of Carbon dioxide.

Pipingmart is B2B portal specializes in industrial, metal and piping products. Also, share latest information and news related to products, materials and different types grades to help business dealing in this industry.