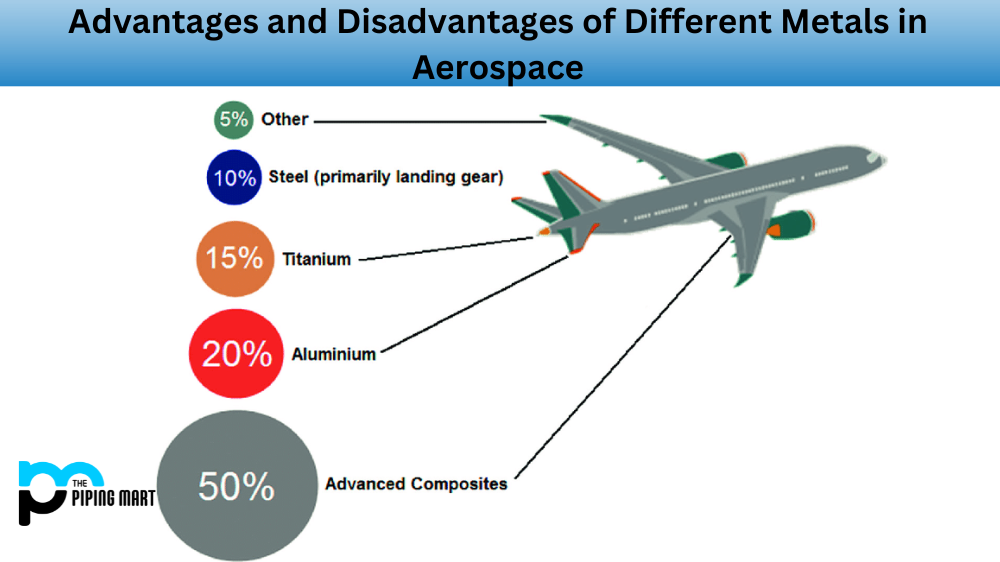
Aerospace engineering is a complex field requiring the application of a variety of materials for use in aircraft components. Many metals are used in the aerospace industry, each with its own unique set of advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will discuss some of these metal materials used in aerospace engineering and their benefits and drawbacks.
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum is one of the most common metals used in aerospace manufacturing due to its lightweight properties and corrosion resistance. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to other metals, making it an attractive option for many applications. Its light weight also allows for greater fuel efficiency compared to other metals such as steel or titanium. Additionally, aluminum is highly ductile and can be formed into complex shapes with ease. However, aluminum has limited strength compared to other materials, so it may not be suitable for certain components that require strength or stiffness.
Titanium alloys
Titanium is another metal widely used in aerospace engineering due to its high strength-to-weight ratio. It also has excellent corrosion resistance, which makes it ideal for use in aircraft components exposed to harsh environments. They have typically used in engine components as well as fuselage skin panels due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures without becoming brittle or losing strength. Additionally, titanium alloys have excellent fatigue properties, which make them ideal for components that experience frequent vibration during operation, such as landing gear struts and wings. The main downside of titanium is its cost; it can be extremely expensive compared to other metals.
Stainless Steel
Steel is another metal commonly used in aerospace engineering due to its high strength and stiffness properties as well as its relatively low cost when compared to titanium or aluminum alloys. Steel also has good fatigue properties, which makes it ideal for use in components such as landing gear or engine mounts that will be subject to frequent loading and unloading cycles during normal operation. Additionally, stainless steel is relatively easy to manufacture and can be formed into complex shapes with ease. The main disadvantage of steel is its weight; steel parts can be much heavier than parts made from lighter materials such as aluminum or titanium alloys.
Conclusion:
Metals are essential components used by the aerospace industry due to their strength, stiffness, corrosion resistance, and affordability, depending on the application requirements. Aluminum offers low cost with good corrosion resistance, while titanium offers a higher strength-to-weight ratio but at a much higher cost than aluminum or steel alloys. Steel provides great fatigue properties at a relatively low cost but can often be too heavy for certain applications. Ultimately, choosing the right metal depends on the specific requirements of each application and requires careful consideration from aerospace engineers and technicians alike. Metals provide structural support while minimizing weight restrictions associated with flight operations. While each type of metal has its own set of benefits and drawbacks, the right combination can provide excellent performance regarding strength, durability, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness – essential factors when designing aircraft components for maximum performance levels! With various metals available today for use in aerospace applications, choosing the right combination can be difficult but ultimately rewarding when successful results are achieved!

Meet Bhavesh, a seasoned blogger with a wealth of knowledge and experience. From metal products manufacturing to retail, Bhavesh has a diverse background in various industries and is dedicated to sharing his insights and expertise with readers.