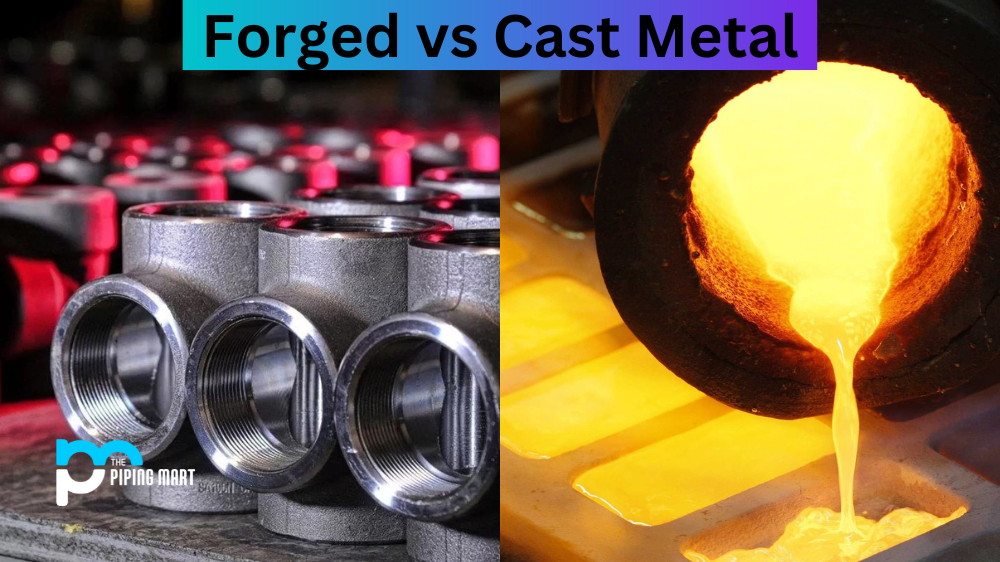
When it comes to metal products, the manufacturing process makes all the difference. Two popular methods for producing metal products are forging and casting. Both techniques have advantages and disadvantages, and knowing their differences can help you make more informed decisions when choosing the right metal for your application. In this blog post, we’ll explore the differences between forged and cast metal, so let’s get started.
Forged Metal
When metal is forged, it is heated and then shaped using a hammer or press. Stamped metal is made by hammering heated metal into the desired shape. This process creates a dense, strong metal product more resistant to wear and tear. Forged products are commonly used in high-stress applications such as aircraft parts, heavy machinery, and automotive components.
Cast Metal
In contrast to forging, casting involves melting the metal and pouring it into a mould. After it cools, the metal takes on the shape of the mould. Cast metal products tend to be less dense than forged ones and can be more porous, making them more prone to wear and tear. Cast products, such as metal sculptures, jewellery, and ornamental gates and railings, are often used in decorative applications.
Difference Between Forged and Cast Metal
Strength and durability
Forged metal is typically stronger and more durable than cast metal due to its denseness and resistance to wear and tear. Forged products are less likely to break or crack under stress, making them ideal for high-stress applications. While less dense and less strong than forged metal, cast metal can still be a good choice for applications where strength and durability are not the primary concerns.
Cost and flexibility
The cost of forging and casting metal can vary depending on several factors, including the size and complexity of the product, the materials used, and the production volume. Forging can be more expensive than casting, but forged metal products are often made to more precise specifications than cast ones. Casting, on the other hand, is usually more flexible than forging, as it allows for more complex shapes and designs.
Choosing the right process
When choosing between forging and casting, there are several factors to consider. For high-stress applications where strength and durability are key, forged metal may be the best choice. For decorative applications, casting may be more appropriate. Cost and production volume can also play a role in the decision-making process. Ultimately, the choice between forging and casting will depend on the specific needs of your project.
Other Differences
- Forged metal is created by hammering or pressing a piece into shape.
- Cast metal is created by pouring molten metal into a mould.
- Forged metal is stronger than cast metal.
- Cast metal is less likely to contain impurities than forged metal.
- Forged metal is more expensive than cast metal.
- Forged metal is more difficult to produce than cast metal.
- Forged metal can be produced in small batches, while cast metal must be produced in large batches.
- Forged metal can be customized more easily than cast metal.
- Cast metal is better suited for mass production than forged metal.
- Forged metal has a more “handmade” look than cast
Conclusion:
So, there you have it – forging and casting are two popular methods for producing metal products, each with benefits and drawbacks. When choosing between the two, it’s important to consider factors such as strength and durability, cost, and production volume. By understanding the differences between forged and cast metal, you can make informed decisions about the materials you use for your projects, ensuring you get the best possible results.

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.