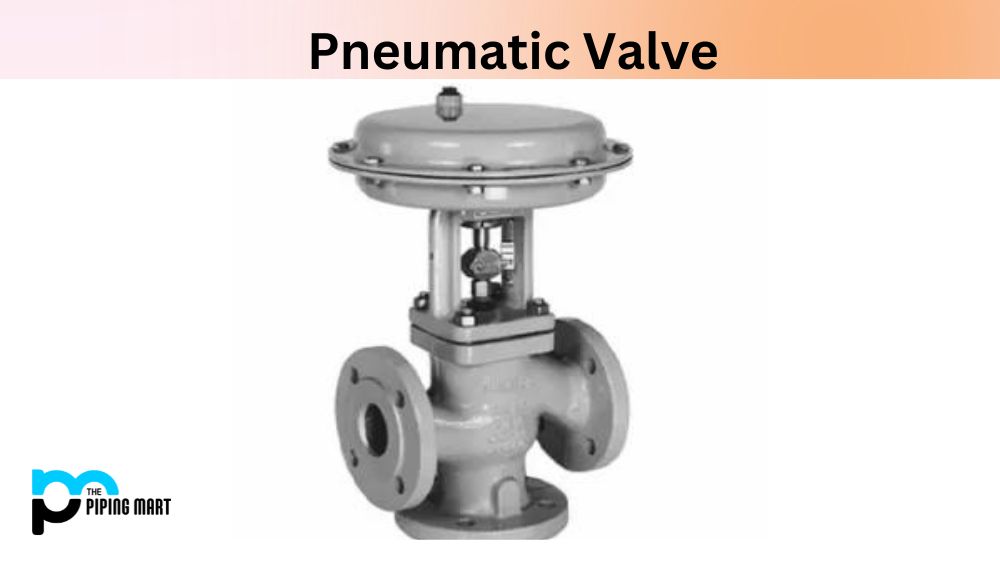
Pneumatic valve technology is a widely used modern industrial control valve that is popular in many industries. Pneumatic valves are ideal for controlling a wide variety of fluids, including water, steam, gas, and oil. The basic concept of a pneumatic valve is simple, an air-powered actuator creates linear motion, which opens and closes a valve. Despite its popular use, there are still some misconceptions about the benefits and drawbacks of this type of valve. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of pneumatic valve technology.
What is Pneumatic Valve?
A Pneumatic valve is a mechanical device used to control the flow of gas or liquid through a pipe. It utilizes an air pressure signal generated by a compressor in order to open and close, thus allowing for precise regulation of the flow rate. Pneumatic valves are commonly used in industrial applications where precision control is essential to ensure safe operation and maximum efficiency.
Advantages of Pneumatic Valve:
Simple and reliable: Pneumatic valves are easy to install and operate, requiring minimal training and maintenance. The technology is also very stable and reliable, making it an ideal choice for processes that must run 24×7.
Energy-efficient: Compared to some of its counterparts, such as electric valves, pneumatic valves use less electricity, making them more cost-effective and energy-efficient.
Cost-effective: In addition to being energy-efficient, pneumatic valves are generally cost-effective compared to other types of valves. They are also durable and easy to repair, with minimal maintenance required.
Wide range of compatibility: Pneumatic valves are compatible with multiple fluids and can also be used in various industries, from manufacturing to HVAC, to name but a few. This flexibility makes pneumatic valves the go-to option for a wide range of applications.
Disadvantages of Pneumatic Valve:
Not suitable for high-load applications: Pneumatic valves are not suitable for high-load applications, such as those that involve pumping viscous fluids or high-pressure steam. Due to this limitation, pneumatic valves are not ideal for the petrochemical industry, for instance.
Prone to leaks: Pneumatic valves are also susceptible to leaks. Air compressors play a major role in the operation of pneumatic valves, and any malfunction or unplanned downtime can lead to valve leaks and significant financial losses.
Challenges around damping: Controlling damping can be a challenge when using pneumatic valves for process control. Damping refers to how fast, or how slow, a valve opens and closes. Pneumatic valves can be slow to operate, which can lead to challenges with maintaining precise control.
Not suitable for every industry: While the pneumatic valve works well across several applications, there are some industries in which it is not suitable, such as the healthcare and food processing industries.
Conclusion:
Pneumatic valve technology is easy to operate, energy-efficient, cost-effective, and compatible with numerous fluids. Despite its advantages, it also has noticeable limitations, including its incompatibility with high-load applications, susceptibility to leaks, and challenges around damping. These issues shouldn’t deter those thinking of using this technology, but they should be kept in mind when making a decision. Overall, pneumatic valves are an excellent option for processes that require stable and reliable control of fluids and gases, where there is a low risk of leaks and where precise control isn’t of utmost importance.

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.