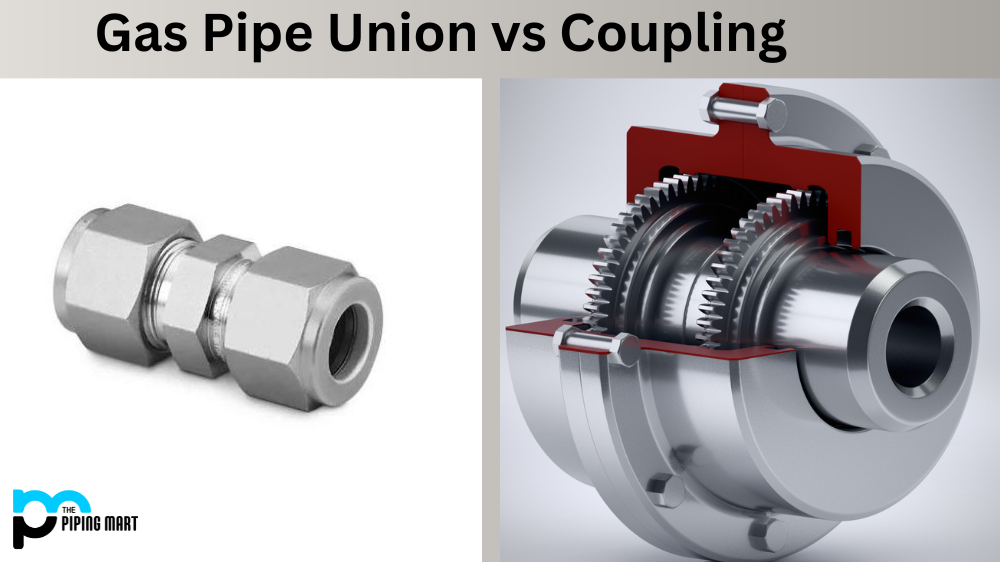
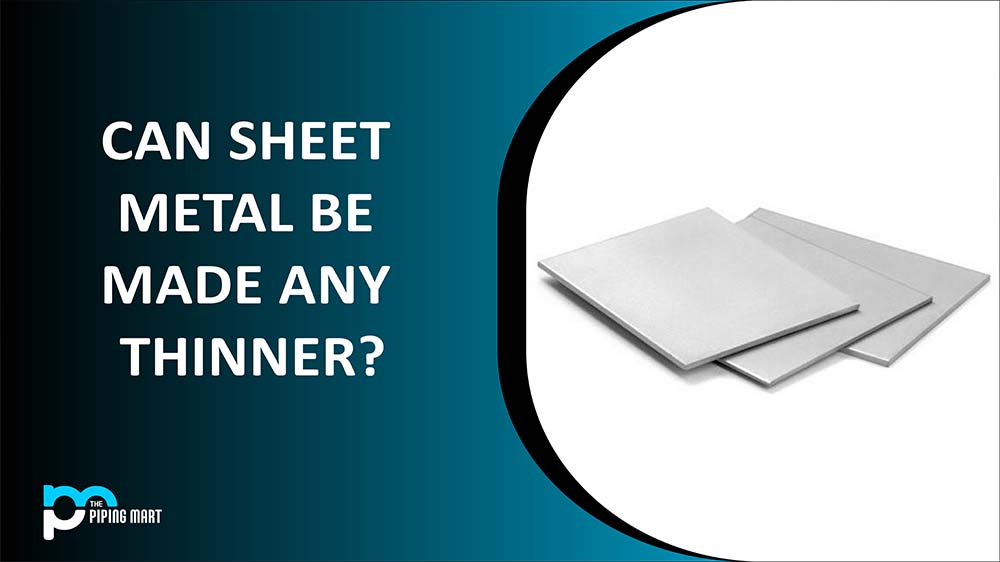
The straightforward response is that non-ferrous metals do not contain iron while ferrous metals do. The more thorough response is that both ferrous and non-ferrous metals have unique characteristics of their own. The applications they are best suited for are determined by these characteristics.
Metals that are not ferrous have been utilized since the dawn of civilization. The Stone Age came to an end and the Copper Age began with the discovery of copper at approximately 5,000 BC. The Bronze Age began with the creation of bronze, a copper and tin alloy. When iron production became widespread around 1,200 BC, people first began to employ ferrous metals. The Iron Age started as a result.
Which Metals Are Ferrous?
Iron, cast iron, wrought iron, alloy steel, and carbon steel are some typical ferrous metals. Because of their tensile strength and longevity, these metals are highly valued. The tallest skyscrapers and longest bridges are made of carbon steel, also known as structure steel, which is a mainstay in the construction sector. Ferrous metals are also utilized in numerous industrial and residential appliances, cars, railroad lines, shipping containers, and industrial piping.
Ferrous metals typically rust easily when exposed to moisture because of their high carbon content. There are two exceptions to this rule: stainless steel is shielded from rust by the presence of chromium, and wrought iron is resistant to rust due to its purity. The fact that most ferrous metals are magnetic makes them ideal for use in electrical and motor applications. Your refrigerator door’s use of ferrous metals enables you to use a magnet to attach your shopping list to it.
-
Steel
Iron is produced into steel by mixing it with carbon, which makes iron harder. As additional components like nickel and chromium are added, alloy steel becomes even more durable. Iron ore is heated and melted in furnaces to create steel. To create steel bars, the steel can is tapped out of the furnaces and poured into molds. Steel is frequently utilized in the manufacturing and construction sectors.
-
Carbon Steel
Compared to other varieties of steel, carbon steel has a higher carbon content, making it harder. In the production of machine tools, drills, blades, taps, and springs, it is frequently employed. It can maintain a cutting edge.
-
Alloy Steel
Chromium, nickel, and titanium are among the metals added to steel alloys to increase strength and durability without adding weight. Essential alloy steel manufactured with chromium is stainless steel. Electrical components, machine tools, and construction all require alloy steel.
-
Cast Iron
An alloy of silicon, carbon, and iron is known as cast iron. Cast iron is tough, brittle, and wear-resistant. It is utilized in stoves, machine tools, car engines, and water pipes.
-
Wrought Iron
The alloy used to make wrought iron contains so little carbon that it is practically entirely iron. Slag is used in the manufacturing process to offer wrought iron superior corrosion and oxidation resistance, but low hardness and fatigue strength. Fencing, railings, agricultural equipment, nails, barbed wire, chains, and a variety of ornamentation are all made of wrought iron.
Which Metals Are Non-Ferrous?
Aluminum, copper, lead, zinc, and tin are examples of non-ferrous metals, as well as precious metals such as gold and silver. Their malleability gives them a significant edge over ferrous materials. They are ideal for gutters, fluid pipes, roofs, and outdoor signage as they are iron free which increases their resistance to rust and corrosion. Last but not least, they are non-magnetic, which is crucial for many electrical and electronic applications.
-
Aluminum
Aluminum is weak, lightweight, and squishy. Aluminum is simple to forge, machine, weld, and cast. Environments with high temperatures are not suitable for it. Aluminum is a fantastic material to utilize when making food cans and aircraft since it is lightweight. Additionally, castings, pistons, automobiles, trains, and kitchenware are all made of aluminum.
-
Copper
Copper is a red metal with excellent malleability, great ductility, and high conductivity for both electricity and heat. Wire and other conductors made of copper are mostly used in the electrical industry. Additionally, it is utilized in bearings, laws, cartridge cases, and sheet roofing. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, are also made from copper.
-
Lead
Low melting point, heavy, pliable, squishy, and with low tensile strength is lead. It is resistant to corrosion caused by numerous acids and moisture. Lead is a common material used in soldering, batteries, electrical power connections, and building construction.
-
Zinc
Zinc has a very low melting point and a modest to low strength. It is easily machined, however, heating might be necessary to prevent crystal cleavage. The most common application of zinc is in galvanizing, which is the process of coating iron or steel with a protective zinc layer to stop rust.
-
Tin
Tin is ductile, highly malleable, and has a low tensile strength. Steel is frequently coated with it to stop corrosion. Tin cans used to hold food are made of tinplate steel. Tin foil was frequently employed to wrap food products in the late 19th century, but aluminum foil has since largely taken its place. Tin brass and bronze can be created by alloying tin with copper.

Pipingmart is B2B portal specializes in industrial, metal and piping products. Also, share latest information and news related to products, materials and different types grades to help business dealing in this industry.