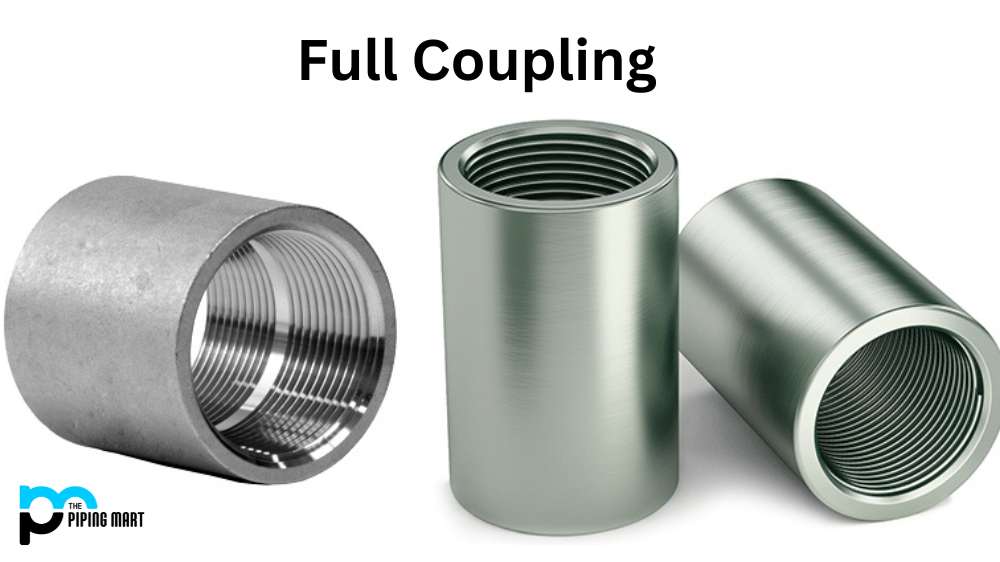
Have you ever heard of full coupling? If not, you’re not alone. Full coupling is a complex process that many people don’t know much about. Today, we’ll break down what full coupling is, the types of full coupling, and its uses of it. Read on to learn more!
What Is Full Coupling?
Full coupling is a process used in engineering to connect two or more components together to improve their overall performance. The connection between these components can be permanent or temporary, depending on the application for which it is used. For example, a car engine is typically permanently coupled to its transmission system to maximize efficiency. On the other hand, a drill press may be temporarily associated with a grinding wheel to sharpen drill bits.
Full Coupling Types
Depending on the application and requirements, several types of full coupling can be used. These include mechanical couplings, hydraulic couplings, linear couplings, pneumatic couplings, and electrical couplings. Each type has unique advantages and disadvantages, which should be considered when selecting one for your application. For example, mechanical couplings are most often used for slow-moving applications due to their low cost and high reliability. In contrast, hydraulic couplings are ideal for high-speed applications due to their ability to absorb shock loads and vibration better than other types of coupling systems.
Full Coupling Uses
Full coupling is used in various industries, including automotive manufacturing, aerospace engineering, industrial machinery manufacturing and more. It can also be used for both short-term and long-term applications, such as connecting two pieces of equipment together during maintenance or repairs or creating an integral part of an overall system that requires reliable operation over time. Additionally, full coupling allows for greater flexibility when designing custom solutions, as it will enable engineers to easily add new components without having to redesign existing systems from scratch. This saves time and money while allowing engineers to create more complex solutions that would otherwise not be possible without full coupling technology.
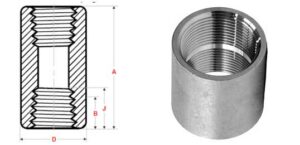
Full Coupling Dimension
| NPS | End to End | Outside Diameter |
Minimum Length of Thread |
|
| A | D | B | J | |
| 1/2 | 48 | 28 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
| 3/4 | 51 | 35 | 12.7 | 13.9 |
| 1 | 60 | 44 | 14.7 | 17.3 |
| 1.1/4 | 67 | 57 | 17 | 18 |
| 1.1/2 | 79 | 64 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
| 2 | 86 | 76 | 19 | 19.2 |
| 2.1/2 | 92 | 92 | 23.6 | 28.9 |
| 3 | 108 | 108 | 25.9 | 30.5 |
| 4 | 121 | 140 | 27.7 | 33 |
Conclusion
Full coupling is a necessary process used by engineers in various industries today. It allows them to easily connect different parts to improve overall performance while providing greater flexibility when designing custom solutions and saving time and money during maintenance or repairs. We hope this article has helped give you a better understanding of what full coupling is, as well as its types and uses, so that you can make more informed decisions about your own projects going forward!
Meet Heer, a dynamic and driven writer learning tricks of her trade in the metal industry. With a background in Digital Marketing, Heer brings a unique perspective to her writing, sharing valuable insights. Apart from blogging she like reading and hiking.