Welding is an essential process used in many industries today. It involves joining two or more pieces of metal by melting them and allowing them to cool, forming a solid joint. However, not all metals are created equal, and welding different types of metals may require other techniques.
Cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel are common metals used in the welding industry. Although they are both made from steel, they have different properties that make them unique. Welding them requires other techniques. In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between welding cold-rolled steel and hot-rolled steel and which is better.
Welding Cold Rolled Steel
To weld cold-rolled steel, you need to take some precautions to avoid defects such as cracking and deformation. Using low heat and avoiding applying too much pressure on the metal during welding is essential. Cold-rolled steel also requires more preparation before welding, where rust, paint, and other contaminants must be removed from the metal surface to prevent the formation of defects.
Welding Hot Rolled Steel
Welding hot-rolled steel requires a higher temperature during the welding process. It also involves using a higher current power source to ensure the weld penetrates the thicker metal. Because hot-rolled steel typically has a rough, uneven surface, cleaning the metal before welding is crucial to achieving good results. Welding hot-rolled steel is ideal for heavy-duty applications, such as construction and metal fabrication.
Difference Between Welding Cold Rolled and Welding Hot Rolled
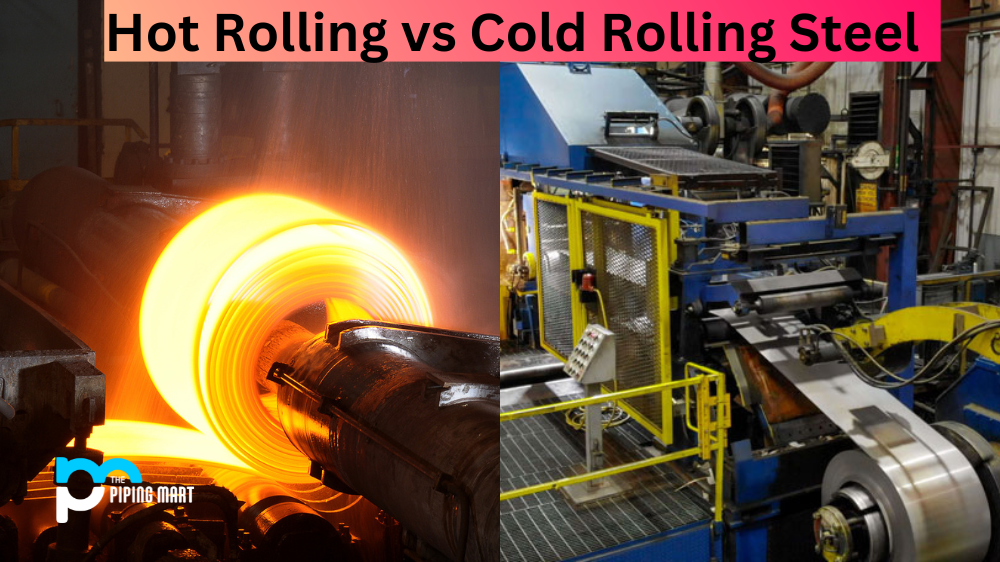
Cold Rolled Steel
Cold-rolled steel is a low-carbon steel that has been cold-rolled to its final dimension, resulting in a smoother and more refined surface. It is used in applications that require a high-quality finish, such as automobile fenders, metal furniture, and electrical appliances. Welding cold-rolled steel requires low heat, as it can quickly become brittle if overheated, leading to cracking and other defects.
Hot Rolled Steel
Hot-rolled steel results from a process that involves heating the steel above its recrystallization temperature and then passing it through a series of rollers. This process forms a rough and uneven surface ideal for heavy-duty applications such as construction and building bridges. Welding hot-rolled steel requires more heat than cold-rolled steel, as it is more ductile and can handle more stress without becoming brittle.
Which is Better?
The choice between welding cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel ultimately comes down to the desired application. Cold-rolled steel is suitable for smooth surface applications, whereas hot-rolled steel is ideal for heavy-duty applications. While cold-rolled steel is more brittle and requires more preparation before welding, hot-rolled steel requires higher heat and can be welded faster. Both types of steel have their benefits and drawbacks, so it’s essential to consider the application and the outcome needed before deciding which to use.
Other Differences
- Cold-rolled steel is steel rolled at room temperature, below its recrystallization temperature. This increases its strength and hardness and decreases its ductility. In addition, cold-rolled steel is often used to create more precise-sized parts, such as automotive body panels and wheel rims.
- Hot-rolled steel is steel rolled at high temperatures above its recrystallization temperature. This makes the steel easier to shape and form. Hot-rolled steel is typically used in applications requiring large sizes or shapes, such as beams or pipes.
- Welding cold rolled steel is typically done with a mig welder using a shielding gas and wire feed speed appropriate for the welded metal thickness. Cold-rolled steel is also commonly welded with tig welding, although this process can be more difficult due to the higher temperatures required.
- Welding hot rolled steel is typically done with a mig welder using a shielding gas and wire feed speed appropriate for the welded metal thickness. Hot-rolled steel can also be fused with tig welding, although this process can be more difficult due to the higher temperatures required.
- Some benefits of welding cold rolled steel include increased strength and hardness, improved dimensional accuracy, and better surface finish. Some benefits of welding hot rolled steel include increased ductility and improved weldability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, welding cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel requires different techniques and precautions. Cold-rolled steel requires less heat and must be adequately prepared before welding to prevent defects, while hot-rolled steel requires more heat and thorough cleaning of the metal to prepare before soldering. Choosing the correct type of steel to use during welding depends on the intended application and desired outcome. By understanding the differences between cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel, you can make an informed decision when choosing the best type of steel to use during welding.

Meet Bhavesh, a seasoned blogger with a wealth of knowledge and experience. From metal products manufacturing to retail, Bhavesh has a diverse background in various industries and is dedicated to sharing his insights and expertise with readers.