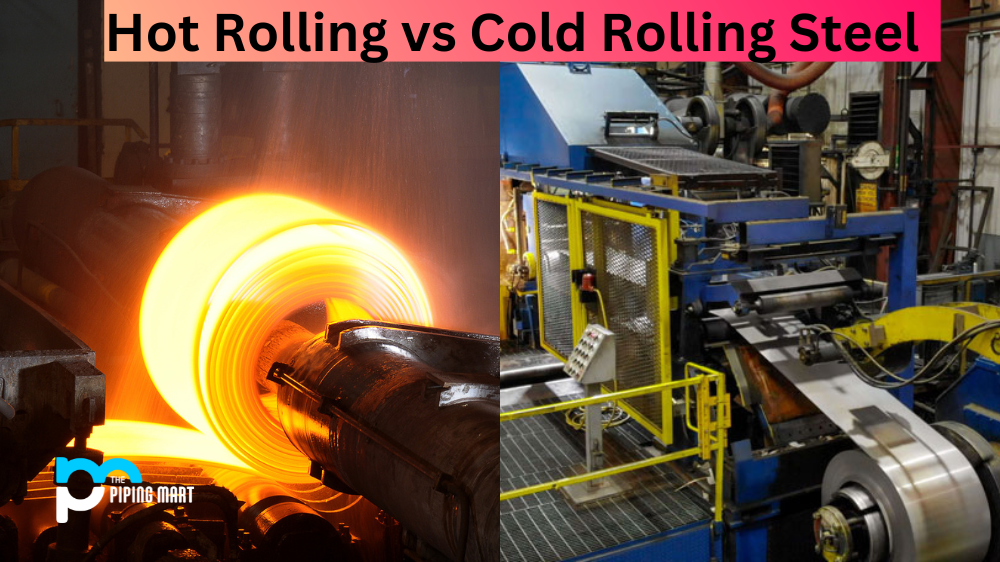
Steel is an important material used in a variety of industries, from construction to automotive. But how do steel producers turn raw materials into the finished product that consumers know and love? The answer lies in two processes called hot rolling and cold rolling. Let’s take a closer look at both processes to learn more about how they work and why they are so important when it comes to manufacturing steel.
Hot Rolling
Hot rolling is the process of heating up a piece of steel until it is malleable enough to be shaped into its final form. This process can be done with several types of metals, but for our purposes, we’ll focus on steel. The process begins by heating up the steel above its recrystallization temperature—typically around 1700°F (926°C)—and then shaping it into its desired form. This can be done with a variety of tools, such as rollers or hammers, depending on the shape that needs to be achieved.
The advantage of hot rolling is that it allows for much faster production times than cold rolling since there’s no need for additional cooling after the metal has been heated and shaped. However, because hot rolled steel isn’t cooled after shaping, it tends to have a rougher texture than cold rolled steel does and will often contain small amounts of scale—an oxide layer that forms during heating—that must be removed before working with the material further.
Cold Rolling
Cold rolling is a process that involves cooling down hot rolled steel before shaping it into its final form. This is done by running the hot rolled metal through rolls at room temperature, which presses out any imperfections like warps or surface scratches, leaving behind only smooth surfaces that are perfect for painting or other decorative treatments. Cold rolling also helps strengthen the metal once it has cooled down; this makes it more durable and less prone to breaking when force is applied during use or transport.
Difference Between Hot Rolling and Cold Rolling Steel
- Hot rolling is a process that involves heating the steel to above its recrystallization temperature. This allows the steel to be easily shaped and formed.
- Cold rolling is a process that involves cooling steel to below its recrystallization temperature. This makes the steel harder and stronger.
- Hot-rolled steel is typically used for applications that require less precise shapes and more forgiving tolerances.
- Cold-rolled steel is typically used for applications that require more precise shapes and tighter tolerances.
- Hot-rolled steel is typically less expensive than cold-rolled steel.
- Cold-rolled steel is typically more expensive than hot-rolled steel.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both hot rolling and cold rolling are essential processes used in producing quality steel products. Hot rolling allows for faster production times, while cold rolling produces smoother surfaces and stronger metals that are more resistant to breakage during use or transport. Understanding these differences between processes can help you make more informed decisions when choosing what type of steel you need for your project!

Abhishek is a seasoned blogger and industry expert, sharing his insights and knowledge on various topics. With his research, Abhishek offers valuable insights and tips for professionals and enthusiasts. Follow him for expert advice on the latest trends and developments in the metal industry.