Regarding anchoring construction and infrastructure, the choice between headed bolts or headed stud anchors leaves many needing clarification and clarification. Both are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, but what makes these options different and how do you decide which is best for your project? This blog will dive into the differences between headed bolts and stud anchors to help you understand the key distinguishing features, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is Headed Bolt?
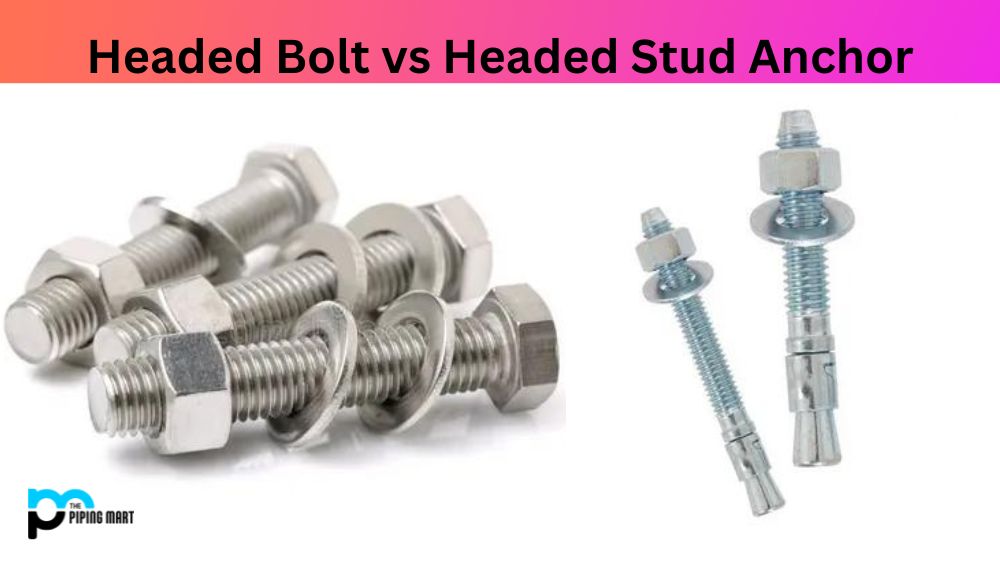
A headed bolt, a lag bolt or a hex head bolt is a fastener typically used for wood construction. They are characterized by their cylindrical shafts that are threaded and have a hexagonal head on one end. The other end may be either partially threaded with blunt edges or fully unthreaded with sharp points for easier insertion into pre-drilled holes. Headed bolts provide strong, secure connections between two pieces of material and can come in various sizes according to the application needed.
What is Headed Stud Anchor?
Headed Stud Anchor is a type of male threaded fastener that is used to attach two materials. It has a head at one end and threads at the other, allowing it to be attached firmly into pre-drilled holes in walls or structural members. The head also provides extra holding strength compared to traditional bolts and screws, making it perfect for heavy-duty applications requiring reliable anchoring.
Difference Between Headed Bolt and Headed Stud Anchor
Design and Application:
Headed bolts, also called anchor bolts, are designed for heavy-duty load-bearing construction projects requiring a secure and robust installation. These bolts include a hexagonally shaped head with a larger surface area for applying torque to fasten the bolt. On the other hand, headed stud anchors consist of a threaded rod (with no head) secured by a cylindrical sleeve drilled and inserted into a pre-drilled hole. They are frequently used in applications where the appearance of the bolt head is not significant and should remain flush with the surface.
Installation and Removal:
Headed bolts are mechanically fastened and often require special pre-drilled holes for installation. They come in different steel grades to withstand different loads and are welded in place to provide extra structural support. Removing a headed bolt is often more challenging than headed stud anchors. On the other hand, headed stud anchors are straightforward to install and can be removed easily, making them an ideal choice in applications with more flexible removal needs.
Cost-effectiveness:
Regarding cost-effectiveness, headed stud anchors are usually the more affordable option, as they are simpler to install, require less material, and often come in larger quantities. Additionally, due to their less robust design, they often do not require the supplemental strengthening measures of headed bolts.
Load-bearing Capacity:
Both head stud anchors and bolts offer excellent load-bearing properties, but the load each can withstand depends on the grade of steel used. Headed stud anchors typically have lower load-carrying capacity as they are less massive than their headed bolt counterparts. However, the advantage of headed stud anchors is that they can be easily installed in confined spaces where threaded bolts cannot be used.
Aesthetics:
The appearance of the installation surface is a vital factor when it comes to choosing between headed bolts and headed stud anchors. Headed stud anchors offer a more streamlined appearance and are ideal for installations where the head of a bolt will come into contact with a sensitive surface in a way that may impact the appearance or flushness of the surface.
Conclusion:
Regarding anchored construction, the decision between headed bolts and headed stud anchors ultimately comes down to your specific application requirements. While both offer advantages and disadvantages, understanding their differences in design, installation, load-bearing capacity, and aesthetic appearance will be critical in determining which option is right for your project. Understanding these fundamental factors and consulting with an expert fastener supplier will ensure your project is structurally sound, cost-effective and meets your specific installation requirements.
Meet Heer, a dynamic and driven writer learning tricks of her trade in the metal industry. With a background in Digital Marketing, Heer brings a unique perspective to her writing, sharing valuable insights. Apart from blogging she like reading and hiking.